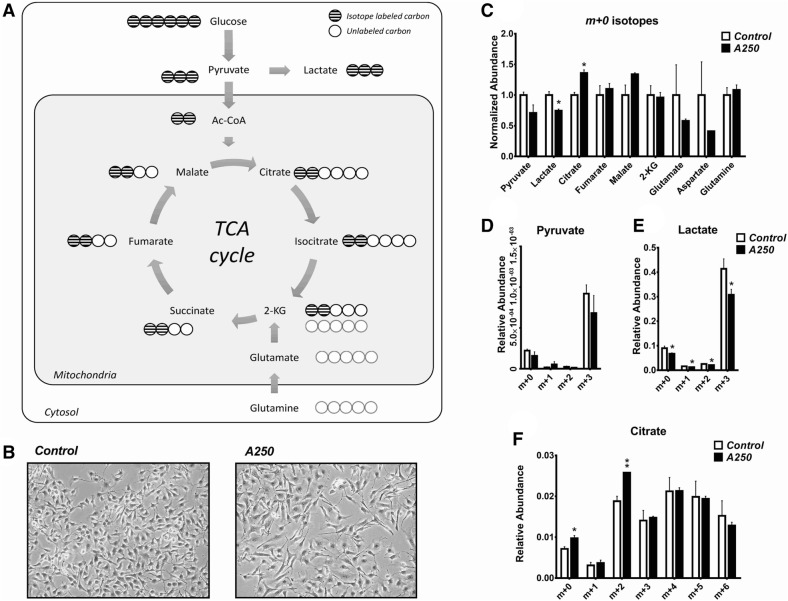
Figure 4.
Metabolomics results. The effect of A250 on the cancer-specific cell metabolism was validated in B16F10 melanoma cells using isotope-labeled glucose. (A) [U6-13C6]-glucose is converted to pyruvate in glycolysis. It can be either transported into the mitochondria and converted to Acetyl-CoA, or converted into lactic acid while still in the cytosol. Either way, all carbons of pyruvate and lactic acid are derived from the isotope-labeled glucose. (B) The treatment reduced the proliferation rate and affected the morphology of B16F10 cells after 24 h incubation. (C) The m + 0 isotopes of the main substrates of the TCA cycle were quantified with GC–MS. The abundance was normalized to the control sample. We detected a significant decrease in lactic acid quantity and a significant increase in citrate quantity. (D) The m + 3 isotope of pyruvate was the most abundant, and the treatment did not change the pyruvate level significantly. (E) The m + 3 isotope of lactic acid was the most abundant, but in this case, the treatment significantly decreased its production. (F) All seven isotopomers of citrate were monitored, and the very significant increase of the m + 2 isotope demonstrates the transport of pyruvate into the mitochondria rather than its conversion into lactic acid (one-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Figure 4A was drawn by GB. Graphpad Prism 5.02 software was used for data analysis.