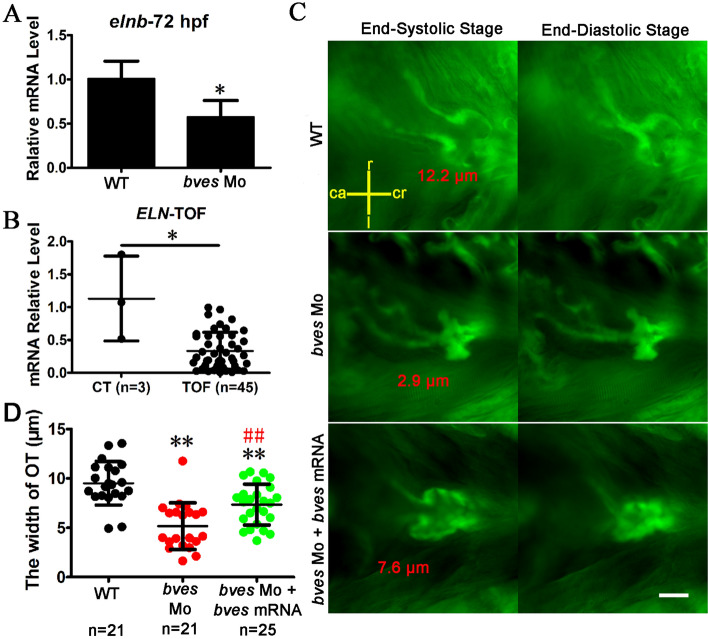
Figure 4.
bves knockdown led to the phenotype of outflow tract stenosis in zebrafish with flia:eGFP. (A) qRT-PCR detected the expression of elnb in zebrafish at 72 hpf. WT, wild type; bves Mo, bves morphants. *p < 0.05. (B) qRT-PCR detected the expression of ELN in human tissue exapmles. CT, control, RVOT tissue of normal controls; TOF, tetralogy of fallot, hypertrophic RVOT tissue of patients. *p < 0.05. (C) bves morphants showed outflow tract defects at 72 hpf in Tg (flia:eGFP) zebrafish. The left column shows the outflow tract at the cardiac end-systolic stage, and the right column shows the end-diastolic stage. The words that marked by red color is the width of outflow tract. ca, caudal; cr, cranial; r, right; l, left. Scale bar = 15 μm. (D) Statistics about the width of outflow at the end-systolic stage in (C). Compared with the WT, the width of the outflow tract in bves knockdown mutants decreased by approximately 50% (WT, 9.5 μm; bves Mo, 5.0 μm, p < 0.01 compared with WT; bves Mo + bves mRNA, 7.5 μm, p < 0.01 compared with WT; p < 0.01 compared with bves Mo). OT, outflow tract; *Significance analysis with WT; #Significance analysis with bves Mo. **p < 0.01; ##p < 0.01. n, number of samples. The error bar shows the mean and SD. bves Mo: bves morphants; WT: wild type; bves Mo + bves mRNA, coinject bves morpholino and bves mRNA.