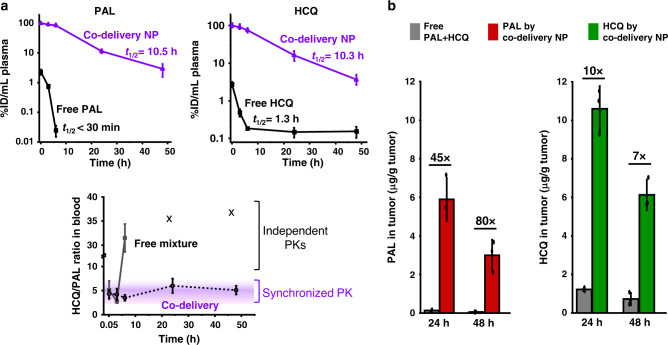
Fig. 3. Co-delivery NP significantly enhanced the synchronized PK and intratumoral distribution of PAL/HCQ pair after i.v. administration in subcutaneous PANC-1 xenograft mice model.
Mice received single i.v. injection of co-delivery NP (with the particle dose of 210 mg/kg) or free PAL/HCQ pair, with an equivalent PAL dose of 10 mg/kg and an HCQ dose of 33 mg/kg that correlated to a PAL/HCQ molar ratio of 1:4.3. a Evaluation of PK profile and PAL/HCQ ratio in plasma. Plasma was collected 0.083, 3, 6, 24, and 48 h post i.v. injection (n = 3 animals included in each data point). The plasma content of PAL and HCQ was determined by UPLC-MS and expressed as percentage of total injected dose (% ID) per mL of plasma. The circulatory half-life (t1/2) were calculated by the PKSolver software. The PAL/HCQ ratio in plasma were calculated and plotted versus time. b PAL/HCQ content at the tumor site. In a separate experiment, mice were sacrificed at 24 or 48 h post i.v. injection (n = 3 animals included in each data point). PAL/HCQ content in tumor site was determined by UPLC-MS, and comparison was made between co-delivery NP and direct administration of free PAL/HCQ mixture. Data were obtained from one set of independent experiment without repetition. Data represent mean ± SD; statistical difference was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. Source data are provided as a Source data file.