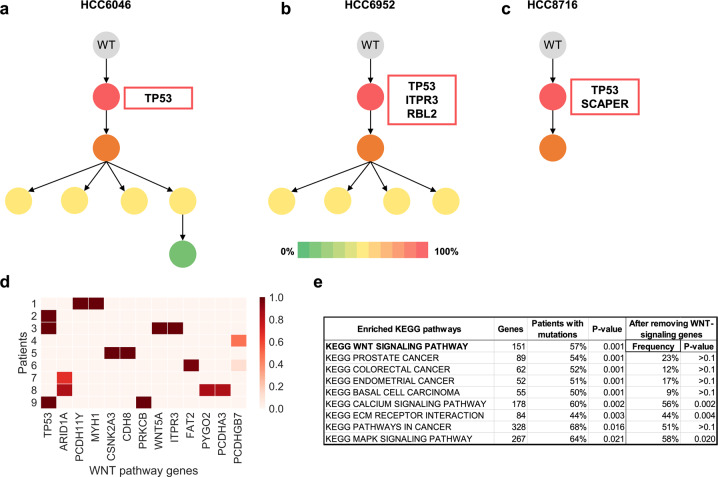
Fig. 5. Inferred tumor phylogenies for HBV-positive HCCs suggest that WNT-signaling pathway mutations play a key role in tumor initiation.
a–c Mutations in TP53 were inferred to initiate tumorigenesis in three of the nine tumors we studied; labels correspond to labeling by Lin et al. d All nine tumors had mutations in WNT-signaling pathway genes that were predicted in the initiating tumor subclone. e The majority of the 102 TCGA-profiled HBV-positive HCCs had mutations in WNT-signaling pathway genes, which was the most significantly mutated KEGG pathway in these patients. Most other significantly mutated pathways were no longer enriched for mutations after the exclusion of WNT-signaling pathway genes from the analysis.