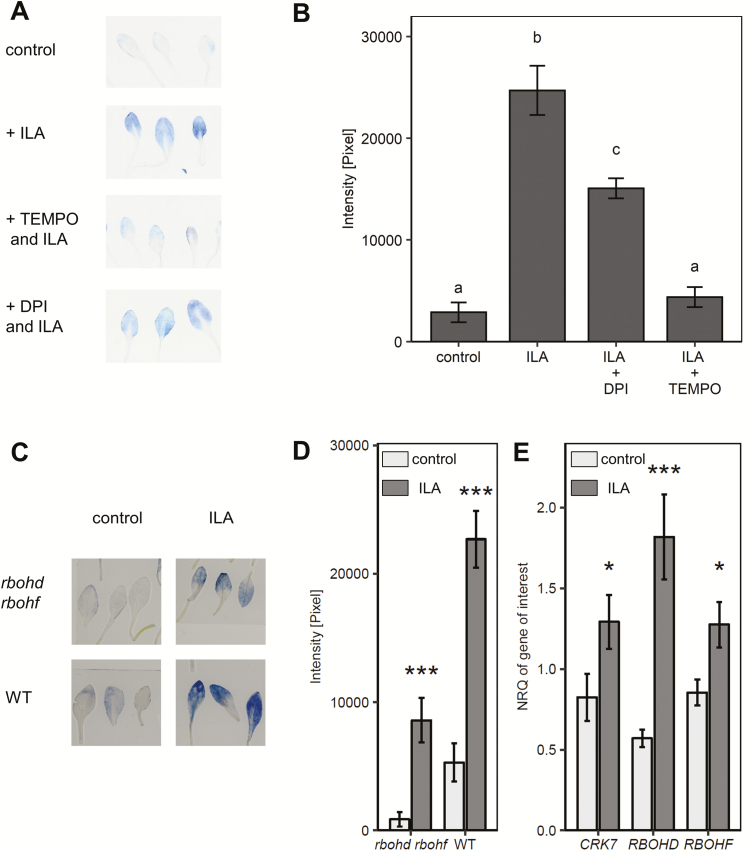
Fig. 4.
NADPH oxidases contribute only partially to ILA-induced superoxide formation in leaves. (A, B) NBT staining is sensitive to superoxide scavenger 4-OH-TEMPO (TEMPO) and reduced by addition of DPI. Twelve-day-old seedlings were treated with 500 µM ILA, with ILA and 4-OH-TEMPO, or with ILA and DPI for 3.5 h. NBT staining of the leaves was determined as a semi-quantitative measurement. Means ±SE; n=9. Significant differences (Padj<0.05) are indicated by letters according to one-way ANOVA. (C) Fourteen-day-old wild type seedlings treated for 48 h either with control medium (light grey bars) or with medium containing 500 µM ILA (dark grey bars). ROS-related genes (CRK7, RBOHD, and RBOHF) were induced by exogenous ILA application in wild type. Gene expression was assessed by RT-qPCR and normalized to S16 and UBQ5. Means ±SE; n=4; differences between treated or untreated plants were analysed by Welch’s two sample t-test. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001. (D, E) O2− radical detected by NBT staining in 14-day-old wild type and rbohd rbohf seedlings treated for 48 h either with control medium (light grey bars) or with medium containing 500 µM ILA (dark grey bars). Means ±SE; n=9. Differences between treated and untreated plants were analysed by Welch’s two sample t-test. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.