Figure 2.
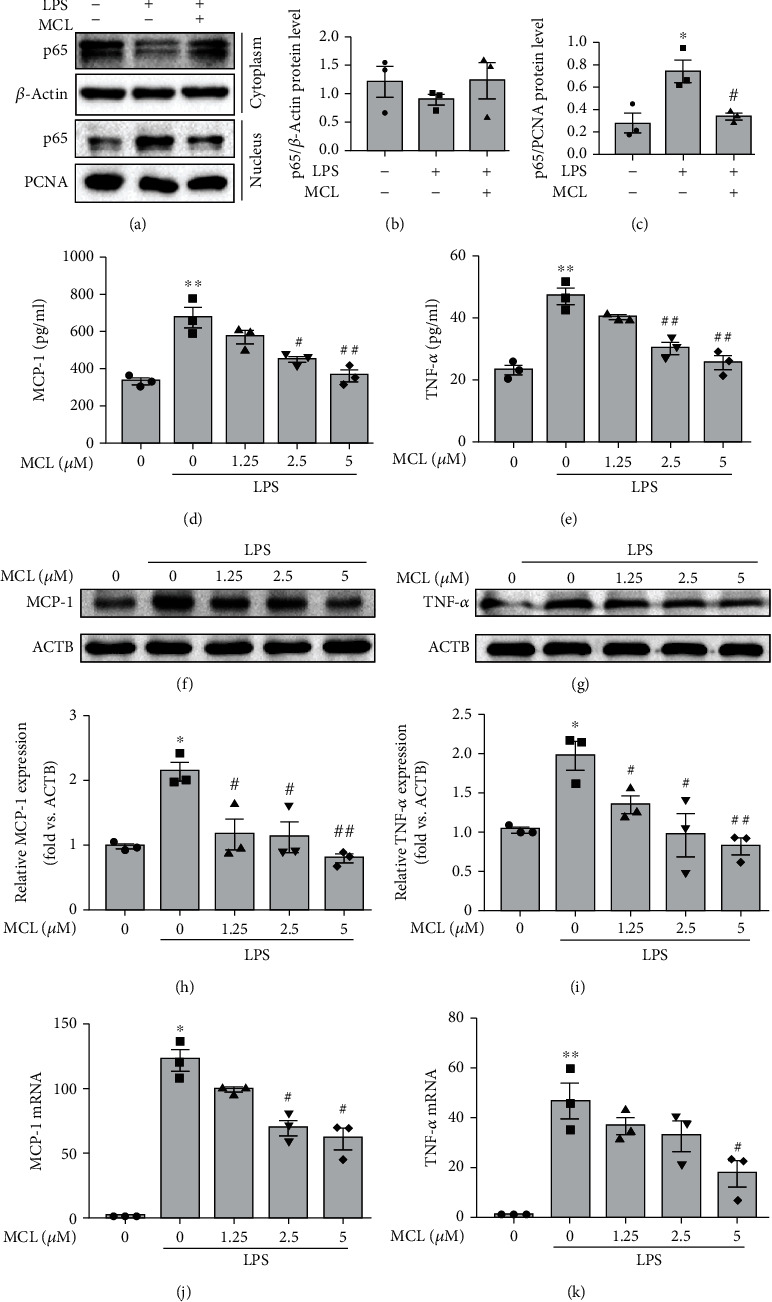
MCL alleviates the LPS-induced NK-κB-dependent inflammatory response in NRK-52E cells. (a) NRK-52E cells were treated with LPS with or without MCL (5 μM). Cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were extracted, and p65 protein expression was detected by western blotting. (b) Cytoplasmic p65 expression relative to β-actin was quantified. (c) Nuclear p65 expression relative to PCNA was quantified. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05 versus normal controls; #P < 0.05 versus the LPS stimulation group. (d, e) ELISA analysis of (d) MCP-1 and (e) TNF-α expression in each group. (f, g) Western blot analysis of (f) MCP-1 and (g) TNF-α expression. (h, i) The relative expression levels of the indicated proteins which were normalized to β-actin (ACTB) expression. (j, k) Real-time PCR analysis of (j) MCP-1 and (k) TNF-α expression in renal tubular epithelial cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus normal controls; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the LPS stimulation group.
