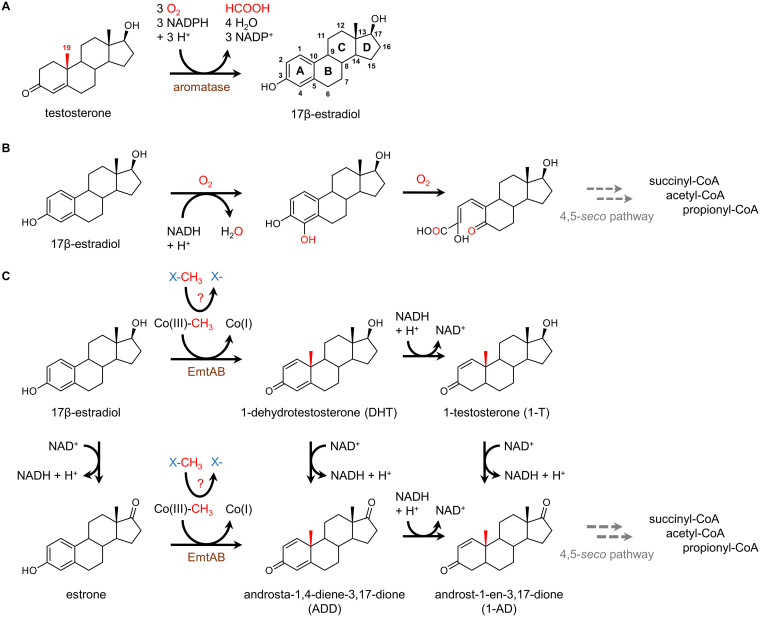
FIG 1.
Biosynthesis in vertebrates and bacterial degradation of 17β-estradiol. (A) O2- and NADPH-dependent aromatization of testosterone to 17β-estradiol in vertebrates catalyzed by Cyp450 aromatases. (B) Aerobic bacterial estradiol degradation involving mono- and dioxygenase-dependent reactions. (C) Proposed 17β-estradiol degradation in denitrifying bacteria initiated by cobalamin-mediated methyl transfer resulting in the retroconversion of 17β-estradiol to 1-dehydrotestosterone that may be reduced to 1-testosterone or oxidized to androsta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione (ADD); likewise, estrone is methylated to ADD. All androgen intermediates are converted to androst-1-ene-3,17-dione (1-AD), the common intermediate of the 2,3-seco pathway. EmtAB, the proposed subunits of estrogen methyl transferase.