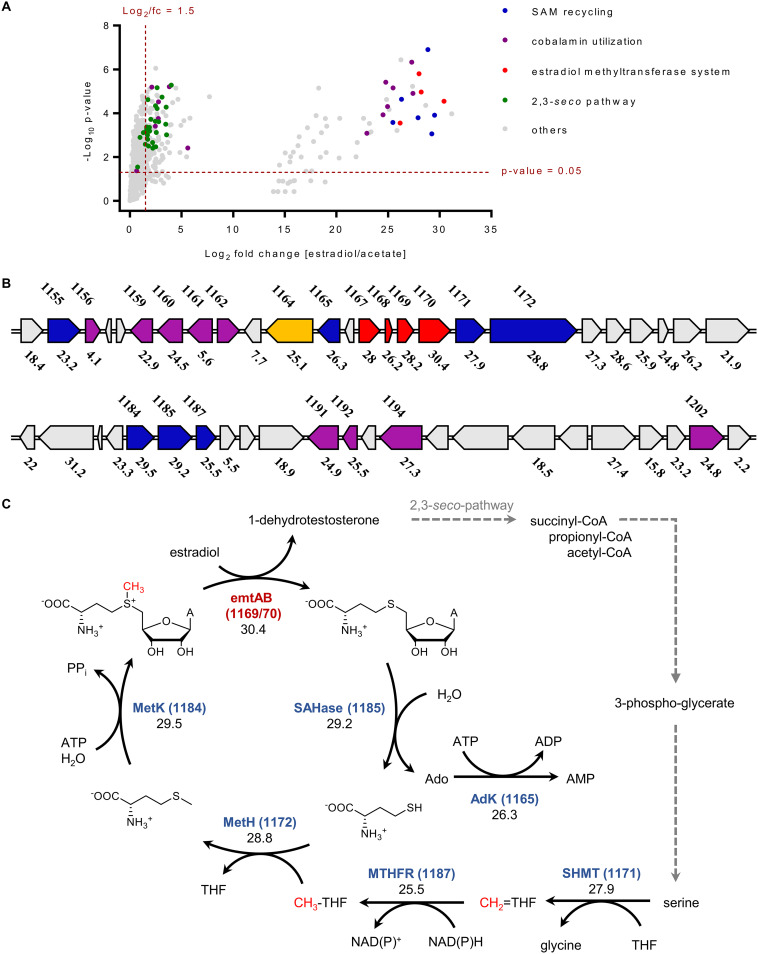
FIG 5.
Differential proteome analysis indicates an estradiol-induced gene cluster involved in estradiol methylation/SAM recycling. (A) Volcano-plot of overall proteomic data (see Table S2 in the supplemental material). Genes were assigned to functions based either on their previous experimental identification or on their higher abundance in estradiol- versus acetate-grown cells, together with similarities to reported genes. The best hits are summarized in Table S3. (B) Estradiol-induced gene cluster comprising genes encoding SAM-regeneration proteins (blue), EMT (red), cobamide utilization/synthesis proteins (purple), and a putative RACE (orange). The numbers shown above the genes refer to gene annotation in the genome of D. oestradiolicum (DENOEST_v1_XXXX), the numbers below to the abundance fold changes in cells grown with estradiol versus acetate. (C) The deduced pathway for directing central C1 metabolism to estradiol methylation by estradiol-induced gene products with fold changes in cells grown with estradiol versus acetate. Abbreviations: EmtAB, estrogen methyltransferase; SAHase, S-adenosylhomocysteinase; MetH, l-methionine synthase; MetK, l-methionine adenosyltransferase; MTHFR, methylene-THF reductase; SHMT, l-serine hydroxymethyltransferase.