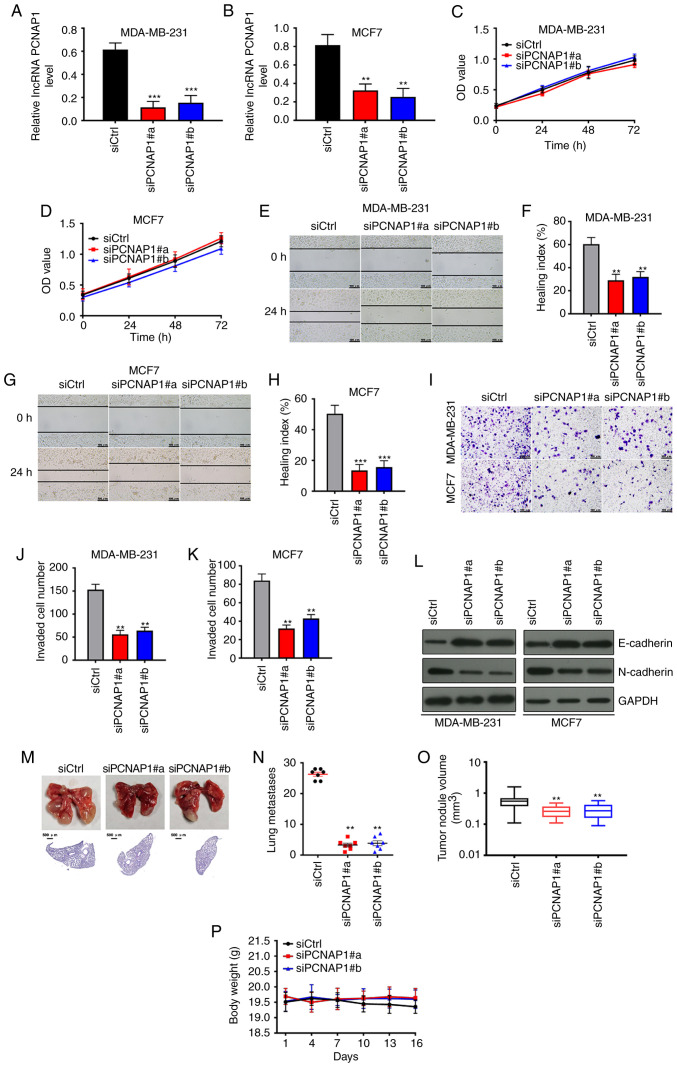
Figure 2.
Knockdown of lncRNA PCNAP1 suppresses the migration and invasion of BC cells in vitro and in vivo. (A and B) Loss-of-function experiments showed that lncRNA PCNAP1 expression levels were markedly decreased following transfection with siPCNAP1#a and siPCNAP1#b compared with scrambled controls (siCtrl) in BC cells (by ~80 and ~70% in MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 cells, respectively). (C and D) Knockdown of lncRNA PCNAP1 had no significant effect on BC cell viability in MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 cells, as confirmed by CCK-8 assay results. (E-H) Loss of lncRNA PCNAP1 significantly decreased the speed of wound closure in BC cells (by ~64 and ~82% in MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 cells, respectively). (I-K) Transwell invasion assays showed that lncRNA PCNAP1 inhibition significantly reduced invasion. (L) Cells with lncRNA PCNAP1 knockdown (siPCNAP1#a and siPCNAP1#b) showed observably increased protein levels of epithelial marker E-cadherin, and decreased levels of mesenchymal marker N-cadherin. (M and N) Injection of siCtrl cells led to lung metastasis in BALB/c nude mice; these metastases were inhibited in nude mice injected with siPCNAP1-transfected MDA-MB-231 cells. (O) Lung metasasis tumor volume of nude mice. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (P) Changes in nude mouse body weight. Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, compared with the siCtrl group. BC, breast cancer; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; PCNAP1, proliferating cell nuclear antigen pseudogene 1.