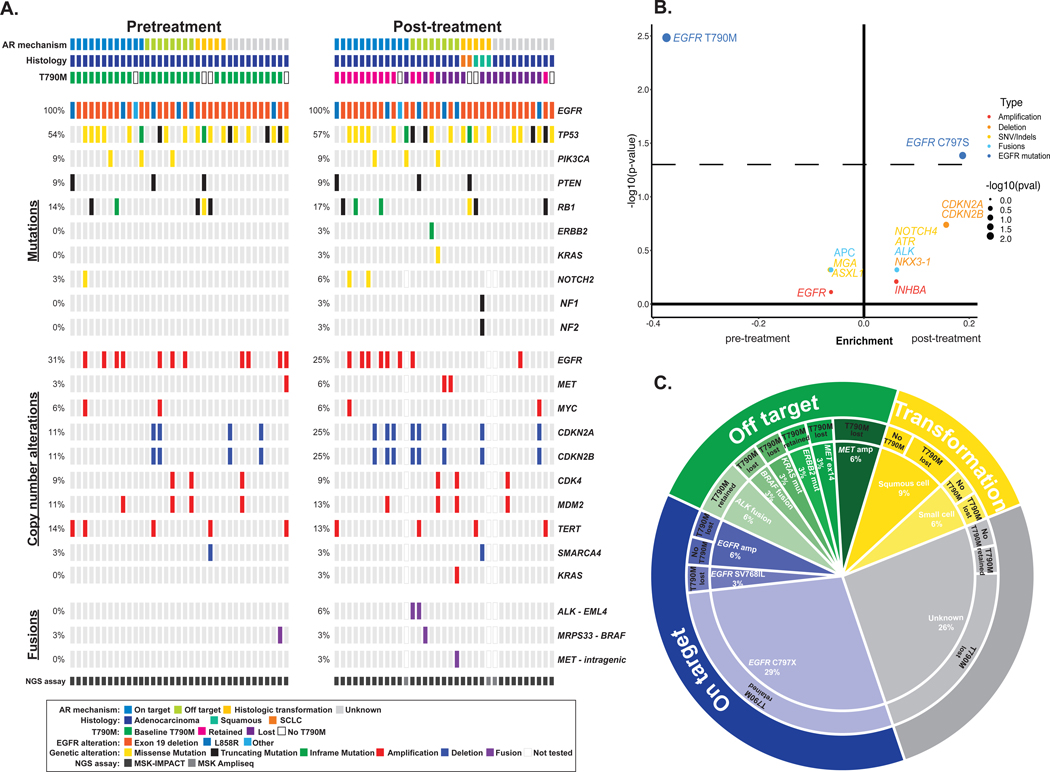
Figure 2. Genomic alterations identified with later-line osimertinib.
A, Frequency of alterations pre- and post-osimertinib in patients treated with later-line osimertinib. The in-figure legend specifies details on acquired resistance mechanism, histology, initial EGFR mutation, alteration type, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) assay. B, Enrichment of individual altered genes pre-osimertinib (left) and post-osimertinib (right). The dashed line represents a P-value of 0.05. the frequency difference between the two sample sets is plotted on the x-axis and its significance [-log10(P-value)] on the y-axis. C, The distribution of established mechanisms of resistance by type of alteration in patients treated with later-line osimertinib. SCLC, small-cell lung cancer; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; AR, acquired resistance