Figure 2.
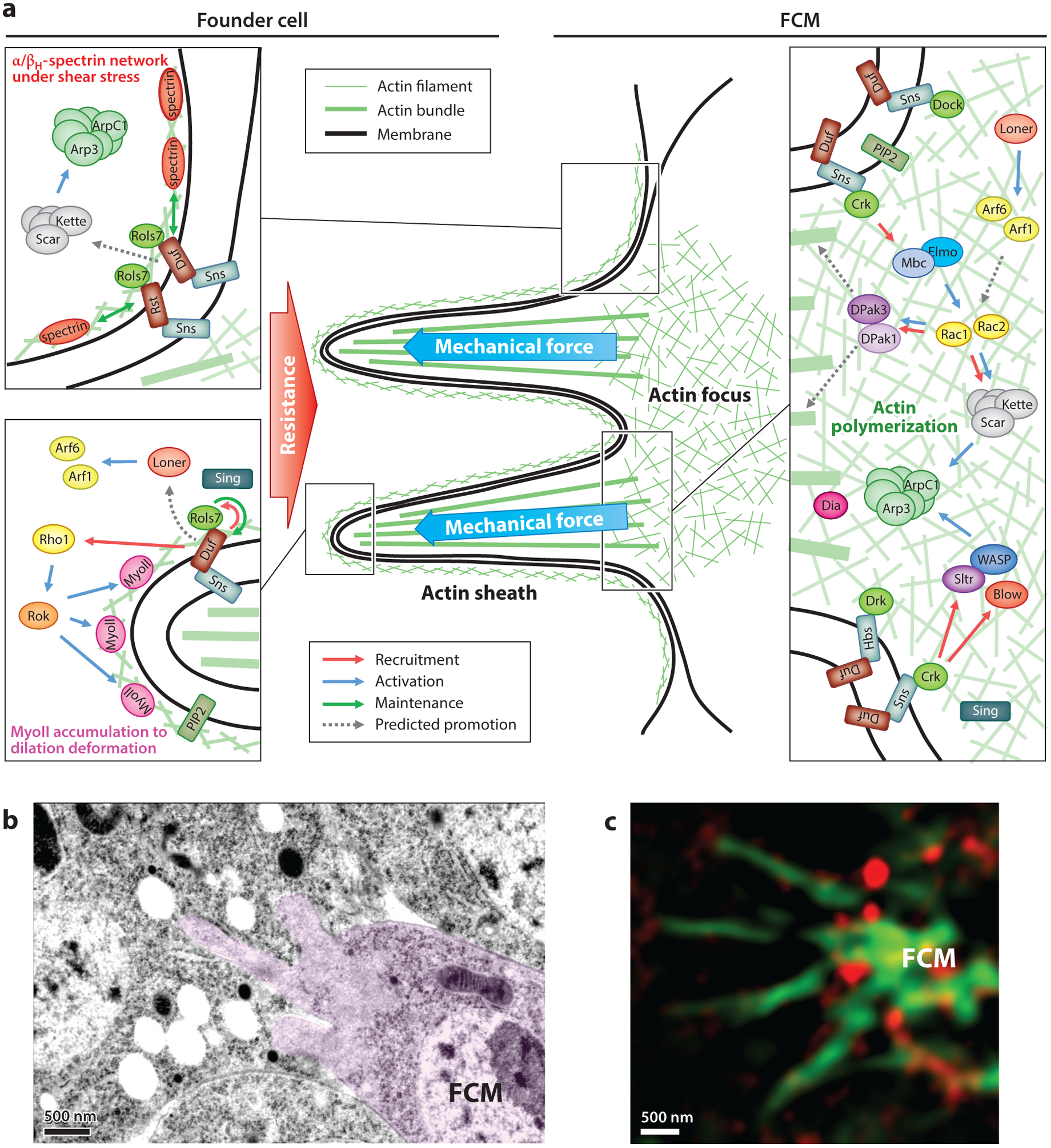
The asymmetric fusogenic synapse. (a) Molecular components and signaling pathways at the fusogenic synapse. Scar, Arp2/3 complex, Loner, Arf, Sing, and PIP2 are shown once in the two founder cell boxes for the sake of simplicity. (b) Invasive protrusions at the fusogenic synapse visualized by transmission electron microscopy. A mononucleated FCM (pink) is projecting membrane protrusions into the binucleated myotube. Note the exclusion of ribosomes and intracellular organelles in the protrusive area, which is filled with actin filaments. Panel b adapted from Reference 114 with permission. (c) The spectrin network constricts the invasive protrusions, visualized by superresolution microscopy. Actin-propelled protrusions (green) from the FCM penetrate through microdomains free of accumulated βH-spectrin (red) in the apposing founder cell. Panel c adapted from Reference 45 with permission. Abbreviations: Arf, ADP-ribosylation factor; Arp2/3, actin-related protein 2/3; βH, βHeavy; Blow, Blown fuse; Crk, Crk oncogene; Dia, Diaphanous; Dock, Dreadlocks; DPak, Drosophila p21-activated kinase; Drk, Downstream of receptor kinase; Duf, Dumbfounded; Elmo, Engulfment and cell motility protein; FCM, fusion-competent myoblast; Hbs, Hibris; Mbc, Myoblast city; MyoII, Myosin II; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; Rok, Rho kinase; Rols, Rolling pebbles; Rst, Roughest; Scar, Suppresser of cAMP receptor/WAVE; Sing, Singles bar; Sns, Sticks and stones; Sltr, Solitary/WIP; WASP, Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein; WAVE, WASP family verprolin homologs; WIP, WASP-interacting protein.
