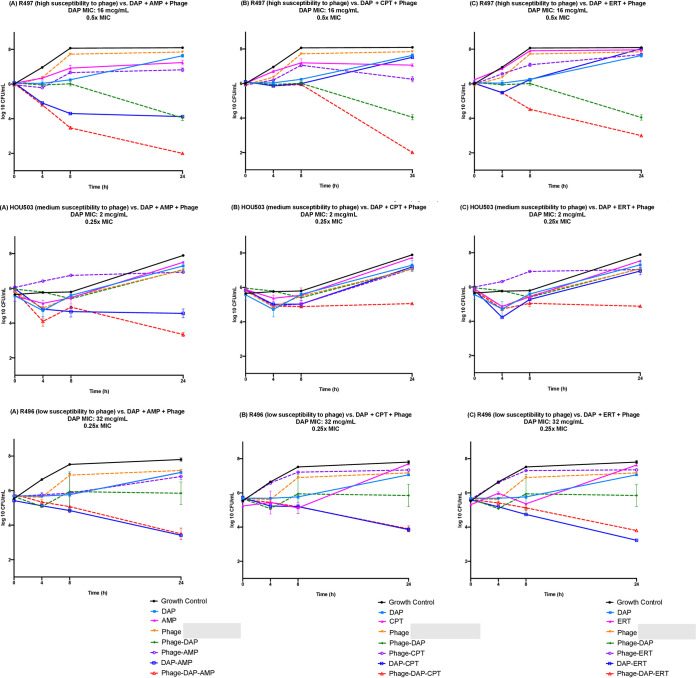
FIG 1.
Time-kill analyses of DAP-AMP, DAP-CPT, and DAP-ERT alone and in combination with bacteriophage against R497 at 0.5× MIC or fCmax (DAP, 8 μg/ml; AMP, 64 μg/ml; CPT, 17 μg/ml; ERT, 15.5 μg/ml) and a theoretical MOI of 0.1, HOU503 at 0.25× MIC or fCmax (DAP, 0.5 μg/ml; AMP, 32 μg/ml; CPT, 8 μg/ml; ERT, 15.5 μg/ml) and a theoretical MOI of 1.0, and R496 at 0.25× MIC or fCmax (DAP, 8 μg/ml; AMP, 16 μg/ml; CPT,17 μg/ml; ERT, 15.5 μg/ml) and a theoretical MOI of 1.0. Synergy was defined as a ≥2-log10-CFU/ml kill compared to the most effective agent (or double-combination regimen) alone at 24 h. Bactericidal activity was defined as a ≥3-log10-CFU/ml reduction from baseline. For R497, bactericidal and synergistic activity was noted with the addition of phage to DAP-AMP (A) and DAP-CPT (B), whereas synergistic activity was noted with the addition of phage to DAP (A to C). For HOU503, synergistic effects were noted with the triple combinations DAP-CPT-phage (B) and DAP-ERT-phage (C). For R496, no enhancement was noted with the addition of phage to DAP-AMP (A), DAP-CPT (B), or DAP-ERT (C). Values are means ± standard deviations.