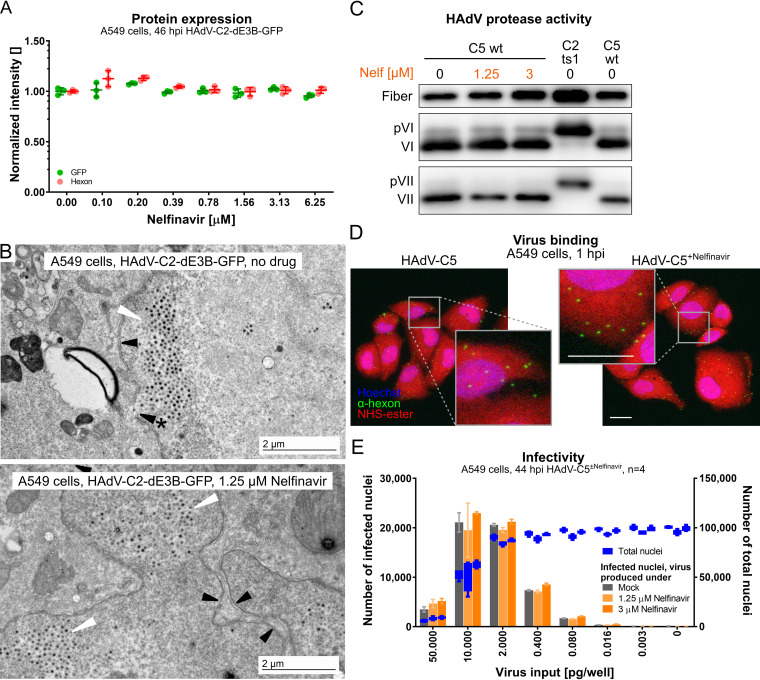
FIG 2.
Nelfinavir does not affect early or late steps of HAdV-C infection. (A) No effect of nelfinavir on the expression of CMV-GFP or the late viral protein hexon in HAdV-C2-dE3B-GFP-infected A549 cells. For each of the four biological replicates, data points represent the mean median nuclear intensities per well normalized to the mean median nuclear intensities of the DMSO-treated wells. Epifluorescence microscopy images were segmented and analyzed using CellProfiler. (B) Representative transmission EM images of late-stage HAdV-C2-dE3B-GFP-infected A549 cells at 41 hpi reveal viral particles inside the nucleus in both DMSO-treated and nelfinavir-treated cells (white arrowheads). Black arrowheads indicate the nuclear envelope, and the arrowhead with * points to a rupture. (C) Nelfinavir does not affect the maturation of HAdV-C5, as indicated by fully processed VI and VII proteins in purified particles grown in the presence of nelfinavir. Note that HAdV-C2-ts1 lacking the L3/p23 protease contains the precursor capsid proteins of VI and VII (pVI and pVII). (D) HAdV-C5 grown in the presence of nelfinavir (HAdV-C5+Nelfinavir) binds to naive A549 cells similarly to HAdV-C5 from control cells. Cells were incubated with the virus at 4°C for 1 h and fixed with PFA. Images are maximal projections of confocal z stacks and also show zoomed-in views (gray squares). Bars = 20 μm. (E) Particles produced in the presence of nelfinavir are fully infectious. A549 cells were inoculated with purified HAdV-C5 and incubated in the absence or presence of nelfinavir for 44 hpi. Shown are data for infection analyses by antihexon immunofluorescence staining and cell numbers derived from Hoechst staining. Bars represent means from four technical replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviations.