Fig. 1.
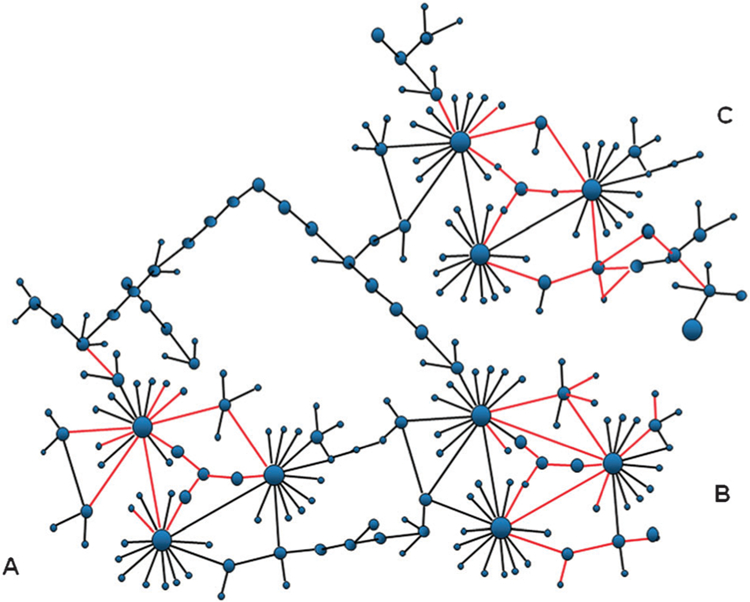
The modular organization of the cellular network can facilitate efficient signaling and cellular response. A node is a protein; an edge a protein–protein interaction. Spatially co-localized proteins are shown with the edges colored in red. Proteins in the module share a function. There are three modules in this network. Many of the interactions within the modules are co-localized in the cell; but no inter-modular interactions. Co-localization saves time because it avoids diffusion–collision in the crowded cellular environment. The most efficient co-localization is via covalent linkage; that is, gene fusion events. Protein–protein interaction is another way to co-localize proteins.
