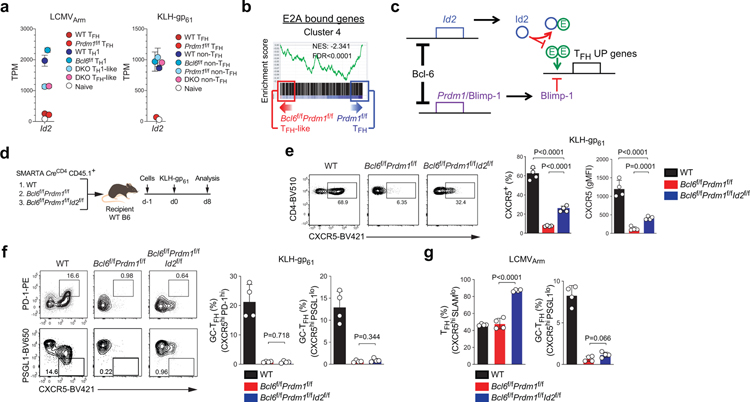
Figure 4. Bcl-6 drives CXCR5 expression via repression of Id2-E2A pathway.
a, Gene expression of Id2 from RNA-seq data of LCMVArm infected mice or KLH-gp61 immunized mice. Each data point was collected from three (LCMVArm) or four (KLH-gp61) independent experiments.
b, GSEA of E2A bound genes from thymocytes22,55 in comparison to Cluster 4 genes between Bcl6f/fPrdm1f/f TFH-like cells and Prdm1f/f TFH cells.
c, A hypothetical model of Bcl-6 regulation of TFH genes primarily via inhibition of Id2 and Prdm1/Blimp-1.
d, Schematic of the SMARTA cell transfer system used for KLH-gp61 immunization. Wild-type, Bcl6f/fPrdm1f/f, or Bcl6f/fPrdm1f/fId2f/f CreCD4 SMARTA CD4+ T were transferred to C57BL/6 host mice, followed by immunization of the host mice with KLH-gp61 in alum + cGAMP, and analyzed 8 days later. See Fig. 4e,f and Extended Data Fig.4a.
e,f, Representative flow cytometry of CXCR5hi TFH, CXCR5hiPD-1hi and CXCR5hiPSGL1lo GC-TFH SMARTA cell subsets from dLNs of KLH-gp61 immunized mice in Fig.4d. Two independent experiments were performed; each dot represents one mouse (n = 4). Data are mean ± s.d., unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test.
g, Quantification of CXCR5hiSLAMlo TFH and CXCR5hiPSGL1lo GC-TFH cells, gated on SMARTA cells from spleens of LCMVArm infected mice. Two independent experiments were performed; each dot represents one mouse (n = 4). Data are mean ± s.d., unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. See Extended Data Fig.4b–g.