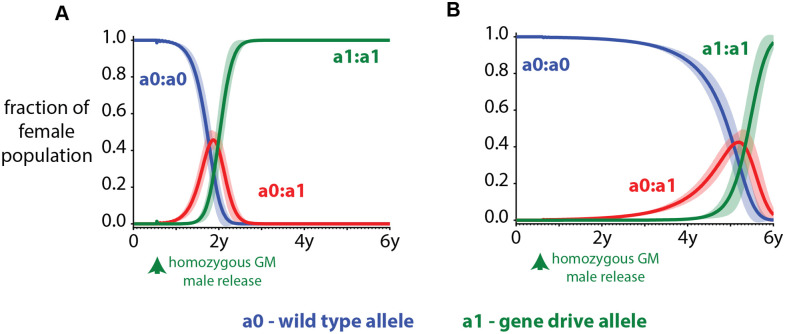
Fig 6. Example of how gene drives behave in the vector genetics model.
The mean (solid line) and one standard deviation (shaded area) of genomes in the population over time of 50 stochastic realizations when male mosquitoes with drive are released into a wild-type population. There is no seasonal variation and no spatial component. Mosquitoes homozygous in ‘a0’ are the wild-type mosquitoes. Male mosquitoes carrying the ‘a1’ allele in a homozygous configuration are released 200 days after simulation starts. The ‘a1’ allele is a driven allele and has a homing rate of 50% to the ‘a0’ site. (A) There are no fitness costs associated with drive mosquitoes. (B) Mosquitoes with drive in either a homozygous or heterozygous configuration have a 10% higher mortality rate than wild-type mosquitoes.