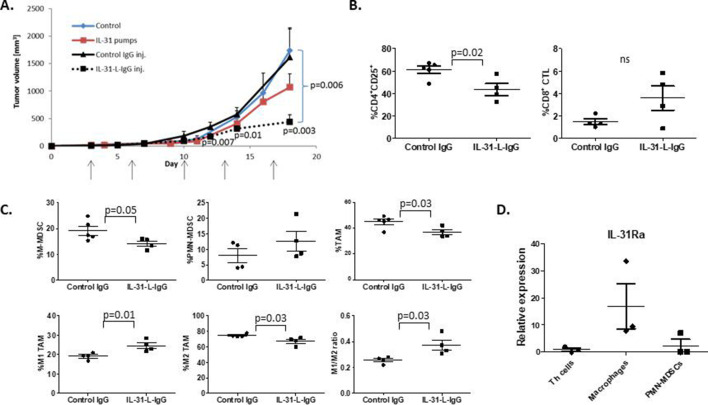
Figure 6.
IL-31 displays potent antitumor activity in vivo. Ten-week-old C57BL/6 female mice were implanted with PyMT cells in the mammary fat pad. After 3 days, mice were intraperitoneally injected with IL-31-L-IgG or control IgG twice weekly (100 µg/inj.). In parallel, another group was implanted with mini-osmotic pumps that delivered purified IL-31 at a dose of 17 µg/day. Control mice were implanted with empty pumps (n=4–5 mice/group). (A) PyMT tumor growth was measured biweekly. (B, C) At endpoint, tumors from mice treated with IL-31-L-IgG or IgG were removed and prepared as single cells. Lymphoid (B) and myeloid (C) populations were analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) Th (CD4+) cells, macrophages (CD11b+F4/80+), and PMN-MDSCs (Ly6CdimLy6G+) were isolated from the spleen of PyMT tumor-bearing C57Bl/6 mice (n=3). RNA was extracted and IL-31Ra mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Relative mRNA levels are present. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way analysis of variance, followed by Tukey post-hoc test for (A) and (D), or by unpaired two-tailed t-test for (B) and (C). Significant p values are shown. CTLs, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; IL, interleukin; IL-31Ra, IL-31 receptor A; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; ns, non-significant; PMN, polymorphonuclear; RT-qPCR, real-time quantitative PCR; TAM, tumor-associated macrophages; Th, T helper.