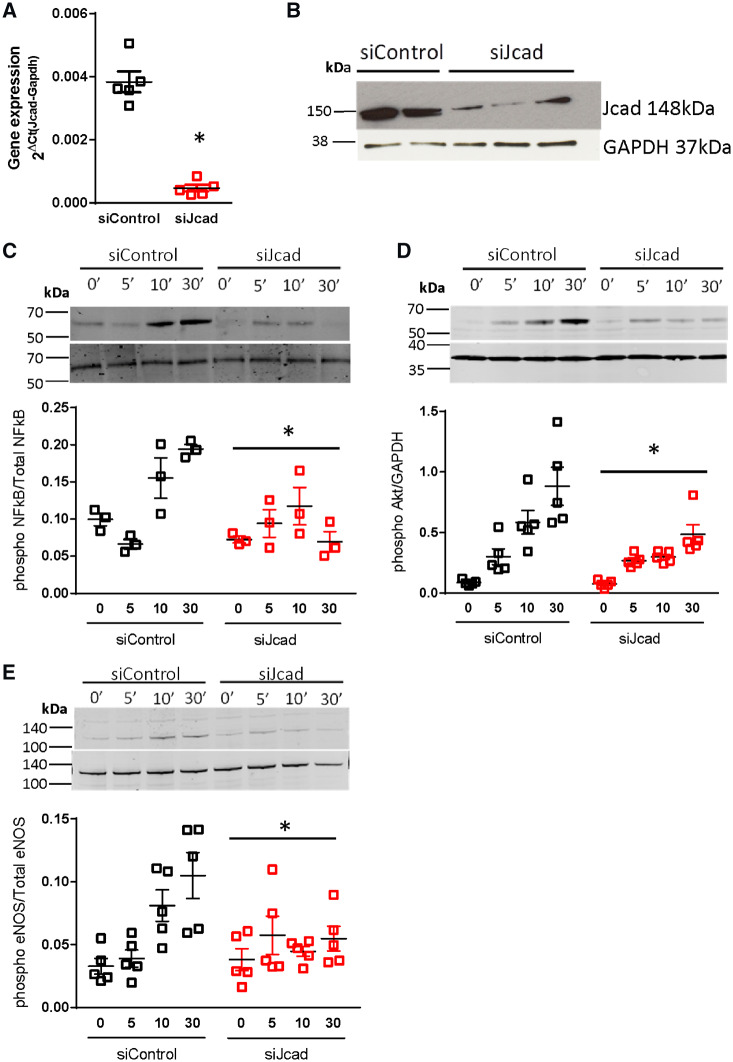
Figure 7.
Knock down of Jcad in primary human aortic endothelial cells leads to an altered response to the onset of flow. siRNA mediated knock down of JCAD (siJcad) lead to a significant decrease in JCAD (A) mRNA (P < 0.05, unpaired T-test) and (B) protein expression (as determined by Western blotting) compared with control cells treated with non-targeted control siRNA (siControl). Control or JCAD knock down cells were plated onto fibronectin coated slides and exposed to shear stress (12 dynes/cm2) for the indicated times or kept as static controls (0–30 min). In siControl, a significant increase in phosphorylation was observed across the time course for all proteins studied (P < 0.05, RM ANOVA). Knock down of JCAD caused a significant blunting in the phosphorylation of (C) NF-КB p65, (D) Akt, and (E) eNOS in response to flow as assessed by Western blot, *P < 0.05, RM ANOVA across time points comparing siControl against siJcad, n = 3–5 per group.