Figure 1.
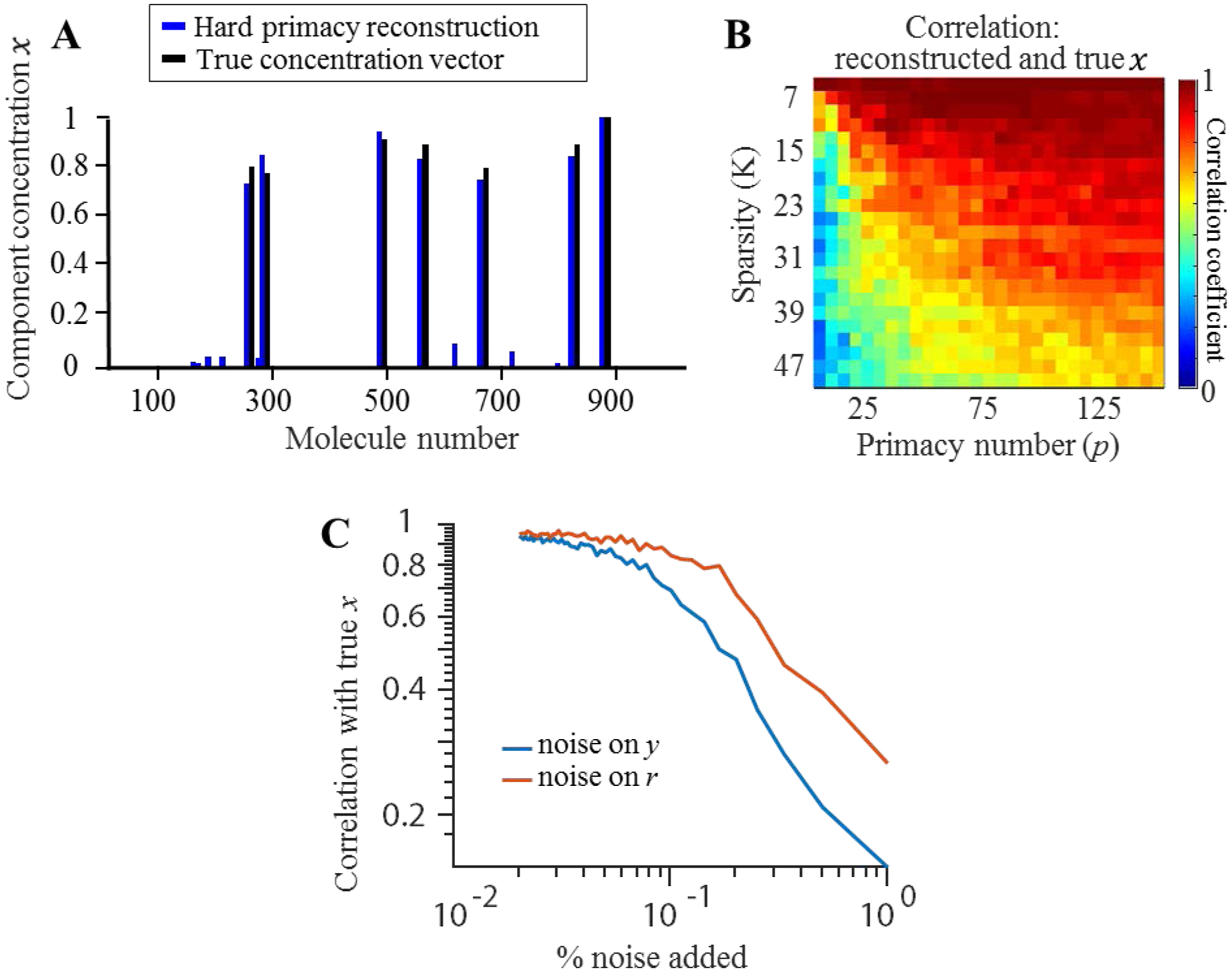
Using relative values of receptor responses can solve the problem of recovering sparse concentration vector . (A) An example concentration vector x alongside its reconstruction (blue) using only relative information that a group of receptors P respond more strongly than the rest. (B) Correlation between the reconstructed and true concentration vectors for different sparsity (K) values and number of primary receptors (p). (C) Correlation between reconstruction and stimulus with various levels of noise injected on input signal(blue) and input neuron response(red).
