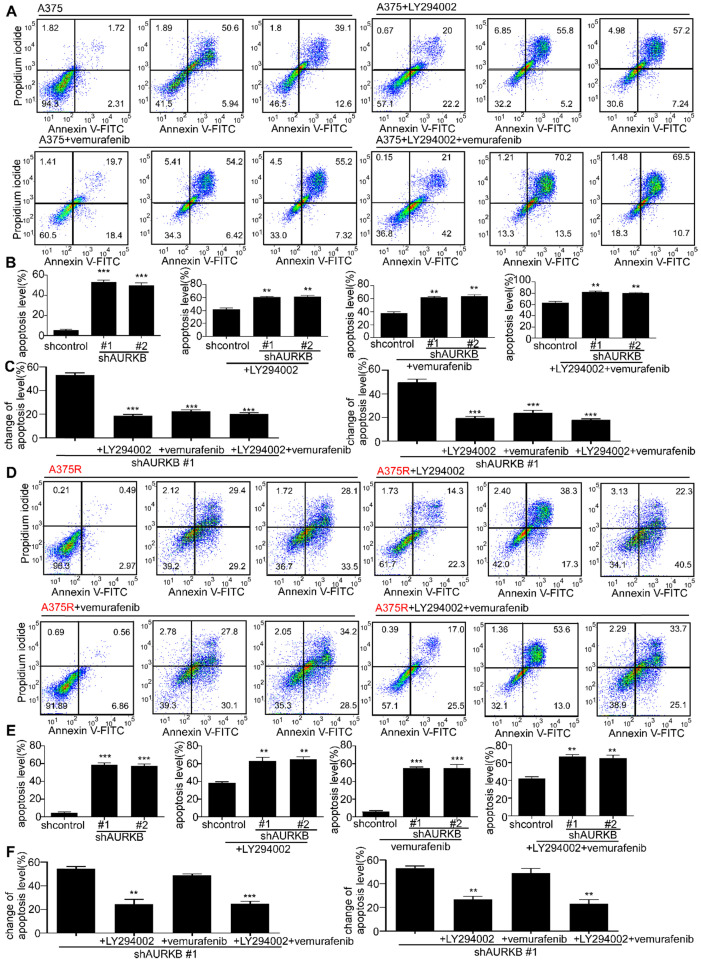
Figure 5.
Knocking down expression of AURKB would induce less additional apoptosis when BRAF/MEK/ERKs and PI3-K/AKT pathways were inhibited. (A, B) The apoptosis rate after knocking down expression of AURKB with non-treatment, LY294002 treatment, vemurafenib treatment and the combination of LY294002 and vemurafenib treatment in A375 cells. (C) The absolute change of apoptosis rate (shAURKB - shcontrol) among A375 cells with non-treatment, LY294002 treatment, vemurafenib treatment and the combination of LY294002 and vemurafenib treatment. (D, E) The apoptosis rate after knocking down expression of AURKB with non-treatment, LY294002 treatment, vemurafenib treatment and the combination of LY294002 and vemurafenib treatment in A375R cells. (F) The absolute change of apoptosis rate among A375R cells with non-treatment, LY294002 treatment, vemurafenib treatment and the combination of LY294002 and vemurafenib treatment. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA and the asterisks indicate a significant change compared with the control group (**, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001).