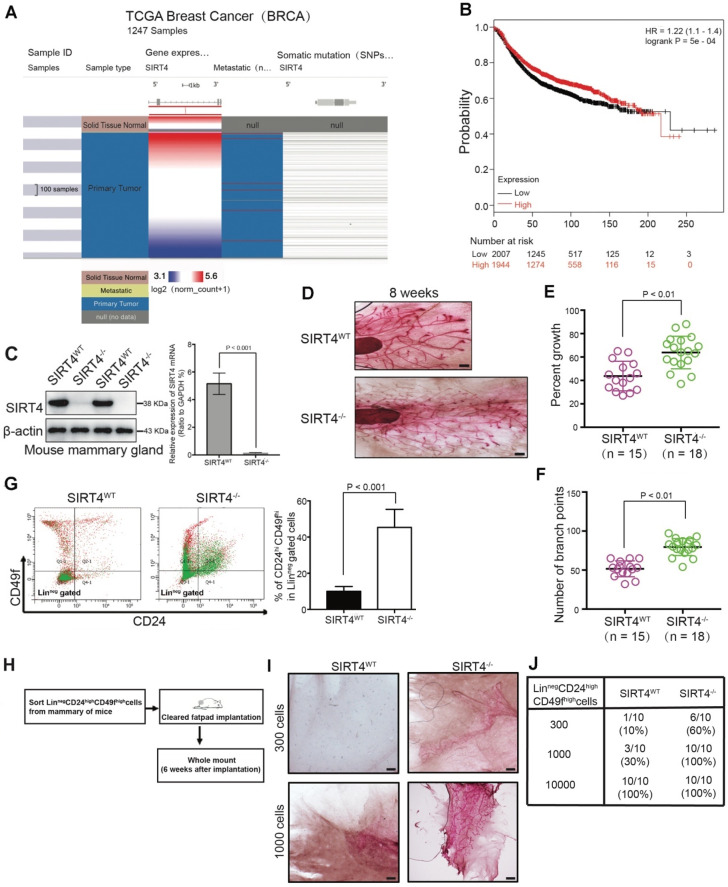
Figure 1.
SIRT4 expression is downregulated in breast cancer and related to mammary gland development and stemness. (A) SIRT4 expression levels in breast cancers compared to healthy tissues from the TCGA data set of 1247 samples. (B) Kaplan-Meier analysis indicating the overall survival of breast cancer patients with high (red) (n = 1944) or low (black) (n = 2007) SIRT4 expression. (C) SIRT4 KO mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory. SIRT4 knockout efficiency was measured by immunoblotting (left panel) and qRT- PCR (right panel). (D) Whole-mount analyses were conducted on 8-week-old SIRT4 wild-type (SIRT4WT) (n = 15), and SIRT4-/- (n = 18) mice and representative images of mammary gland side-branches are shown. (E) Percent of growth. (F) The number of mammary gland side-branches was quantified. (G) Distribution of Linneg mouse mammary cells according to their expression of CD24 and CD49f was analyzed on 8-week-old SIRT4-/- mice and littermate controls (left). Mammary stem cells (MSCs), according to their expression of CD24hiCD49fhi in Linneg (right), were quantified by a flow cytometric analysis. (H, I and J) Schematic representation of limiting dilution transplantation experiments with LinnegCD24hiCD49fhi MSCs (H). A total of 300, 1000, or 1 x 104 LinnegCD24hiCD49fhi MSCs isolated from 8-week-old SIRT4-/- mice and littermate controls were injected into the cleared fat pad of 3-week-old FVB/NJ female mice. Whole-mount analyses were then conducted at 6 weeks after injection (I, J). Representative images of mammary gland side-branches are shown (I). The resulting data were analyzed by the Chi-square test (p < 0.001) (J). Scale bars, 100 µm (D) and 50 µm (I).