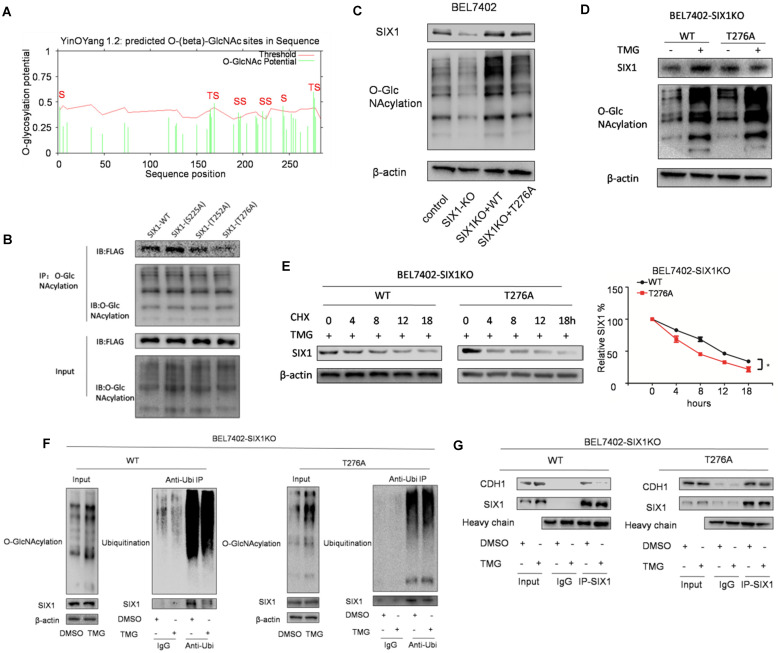
Figure 6.
Mutation in Thr276 decreases the O-GlcNAcylation of SIX1. A The O-GlcNAcylation sites of SIX1 predicted by the YinOYang 1.2 server (www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/YinOYang) are shown with a black arrowhead at the top. The green vertical lines show the potential O-GlcNAc-modified Ser/Thr residues, and the red horizontal wavy line indicates the threshold for modification potential. B The level of SIX1 protein in IP-O-GlcNAcylation samples from BEL7402 cells transfected with plasmids expressing wild-type or O-GlcNAcylation site mutant was analyzed by western blot. C The establishment of SIX1 WT and T276A cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system and subsequent ectopic expression. D The wild-type and T276A SIX1 expression was detected in BEL7402-SIX1KO cells transfected with WT or T276A SIX1-expressing plasmids under the treatment of DMSO or TMG. E Levels of wild-type and T276A SIX1 were determined by western blot in BEL7402-SIX1KO cells transfected with WT or T276A SIX1-expressing plasmids after TMG and CHX treatment for the indicated times. F Ubiquitination of wild-type and T276A SIX1 were examined in BEL7402-SIX1KO cells transfected with WT or T276A SIX1-expressing plasmids. MG132 and NEM were used to inhibit proteasome and deubiquitination, respectively. G CDH1 was detected in purified wild-type and T276A SIX1 IP samples in BEL7402-SIX1KO cells transfected with WT or T276A SIX1-expressing plasmids. (The data from E were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).