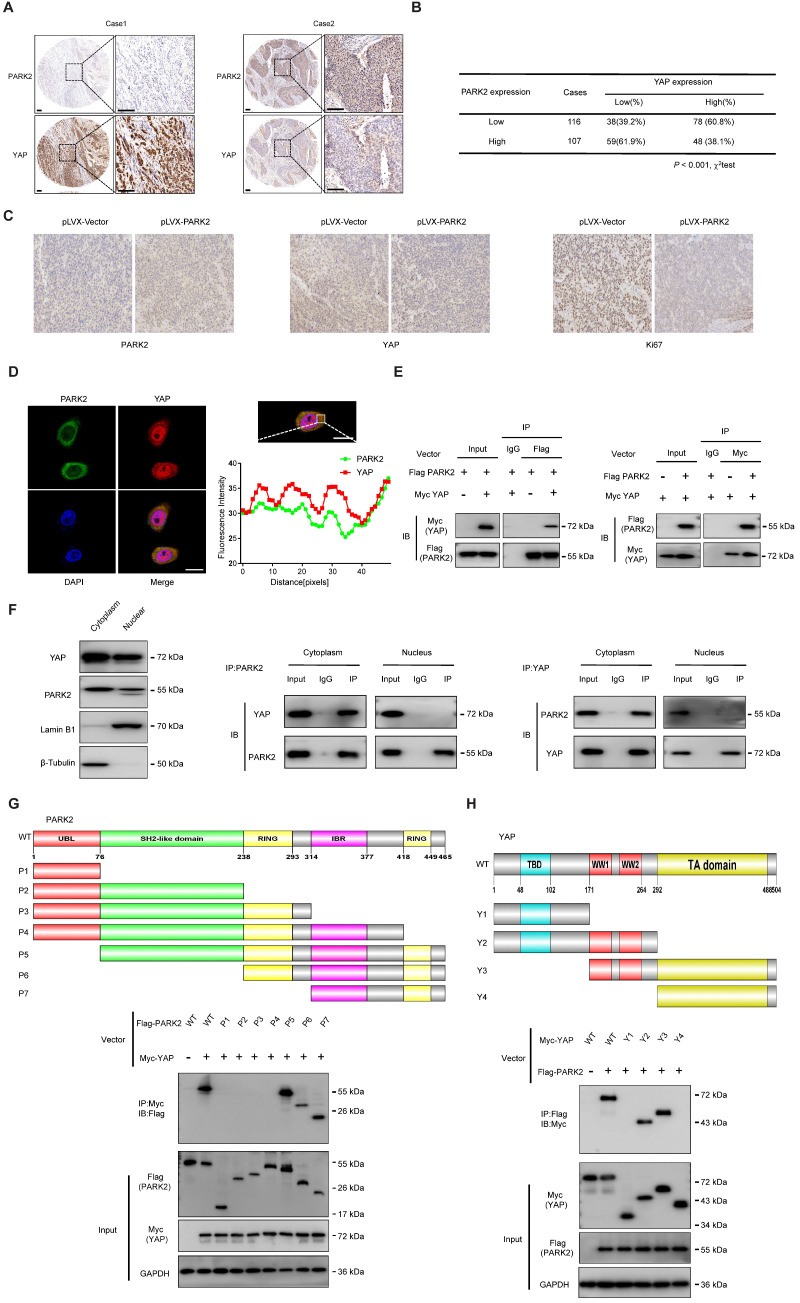
Figure 3.
PARK2 expression is negatively correlated with YAP and interacts with YAP in ESCC cells. A and B. Low PARK2 expression was significantly correlated with increased YAP levels in ESCC specimens analyzed by IHC staining. Scale bar, 100 µm. C. The negative correlation between YAP and PARK2 expression in xenograft tumors, which is analyzed by IHC staining. Scale bar, 100 µm. D. IF showed that co-localization of PARK2 (red) and YAP (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 µm. The fluorescence-integrated density was measured by ImageJ software; while the mander's co-localization coefficients were measured by Zen software. The mean co-localization coefficient=0.77± 0.03. E. PARK2 interacted with YAP in ESCC cells. F. PARK2 is mainly localized in the cytoplasm. The subcellular protein fractionation kit was used for cytoplasm and nuclear separation. Tubulin and Lamin B1 were used for cytoplasm and nuclear control. PARK2 interacted with YAP in cytoplasm. G. PARK2 bound to YAP at its Ring domain. (Top panel) Schematic representation of vectors expressing Flag-tagged wild-type or serial deletion mutants of PARK2. (Bottom panel) The Ring domain of PARK2 interacted with YAP. H. YAP bound to PARK2 at its WW domain. (Top panel) Schematic representation of vectors expressing Myc-tagged wild-type or serial deletion mutants of YAP. (Bottom panel) The WW domain of YAP interacted with PARK2.