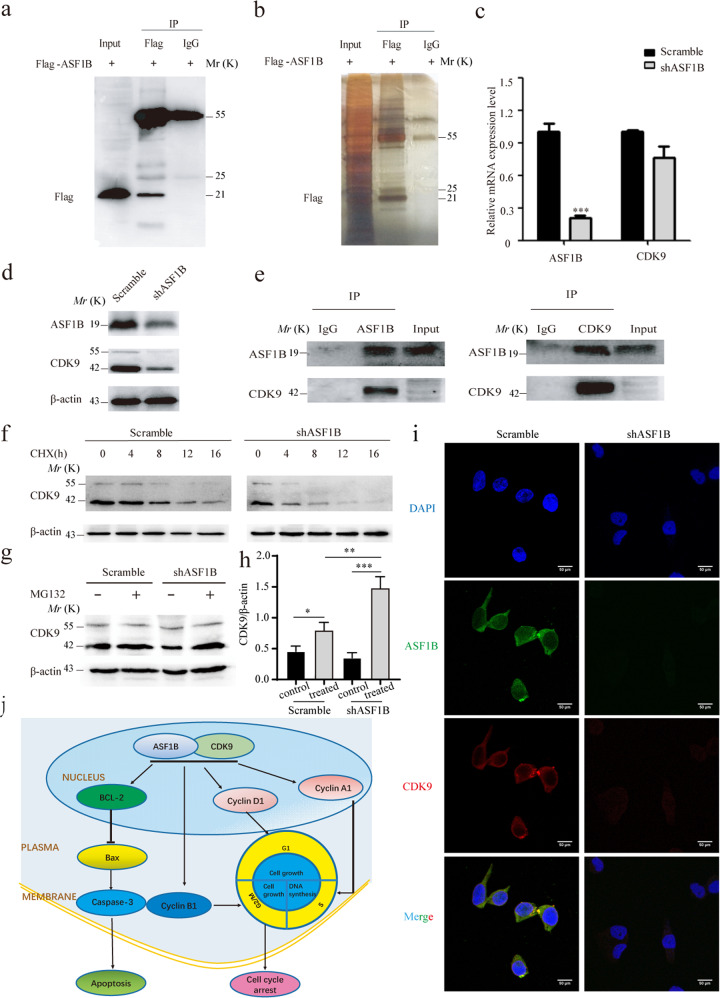
Fig. 6. Interaction of ASF1B and CDK9.
a Western blots were performed to confirm the IP efficiency. b SDS-PAGE was conducted to analyze the production of IP. c Levels of CDK9 mRNA expression in stable ASF1B-shRNA HeLa cells. d. Protein expression of CDK9 in stable ASF1B-shRNA HeLa cells. e. Co-IP was performed to detect CDK9-ASF1B using anti-ASF1B beads and anti-CDK9 beads. f ASF1B-shRNA-HeLa cells or scrambled cells were treated with CHX at 20 μg/ml for 0, 4, 8, 12, and 16 h, and then the CDK9 expression level was determined by western blot. g ASF1B mediates stabilization through the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. ASF1B-shRNA HeLa cells or control cells were treated with proteasome inhibitor MG132 at 5 μM for 4 h, and then the CDK9 expression level was examined by western blot. h Quantification of the results in (d). Data are mean ± SEM, n = 3, and two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test was used. ***p < 0.001. i Colocalization of ASF1B and CDK9 in the nucleus. Immunofluorescent staining and imaging were used to visualize the colocalization of ASF1B (green fluorescence) and CDK9 (red fluorescence) in stable ASF1B-shRNA HeLa cells and corresponding scrambled cells. j A schematic model of this work. A schematic diagram showing the signaling pathway of the ASF1B-mediated effect on cervical cancer cell growth via the ASF1B/CDK9 axis.