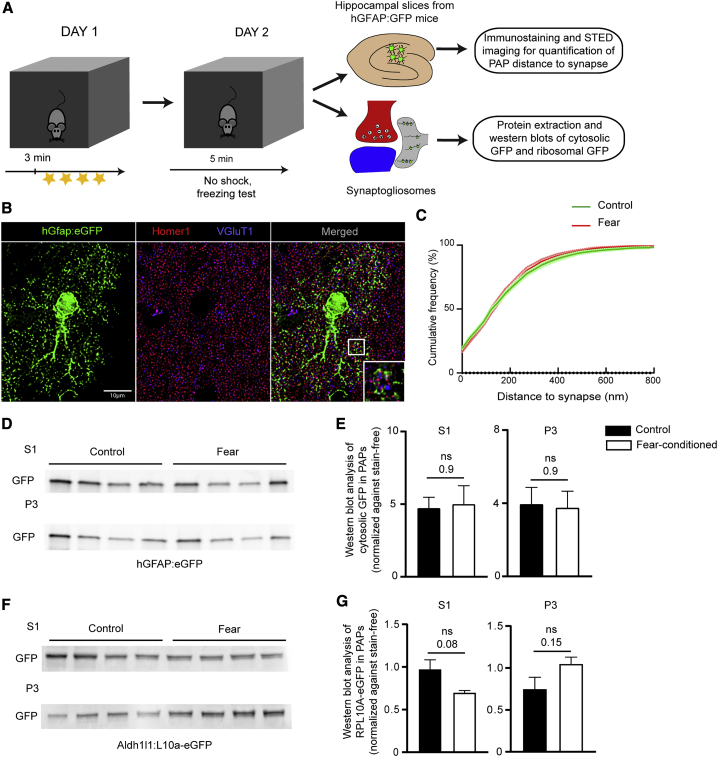
Figure 5.
Characterization of PAPs upon Fear Conditioning
(A) Flowchart for the fear-conditioning protocol, followed by analyses of the PAP-to-synapse distance and PAP proteins in dorsal hippocampus synaptogliosomes.
(B) Deconvoluted confocal microscopy image of a single plane containing an astrocyte and synapses in the dorsal hippocampus of a control hGfap-eGFP mouse. The astrocyte is immunolabeled for eGFP. Pre- and post- synapses are immunolabeled for VGluT1 (blue) and Homer1 (red), respectively. The magnified area shows the STED image for VGluT1 and Homer1 merged with deconvoluted confocal image for eGFP. Scale bar: 10 µm
(C) Cumulative frequency of eGFP as a function of the distance to the synapse (from 0 to 800 nm). Solid lines represent the calculated means, and dotted lines represent the SEM for astrocytes from control mice (green) and fear-conditioned (red) mice. n ≥ 270 synapses per cell, three cells per mouse, and three mice per condition. Two-way ANOVA, interaction value, p = 0.5 (not significant).
(D) Western blot analysis of S1 (whole dorsal hippocampus extracts) and P3 (synaptogliosomes) (Figure 2) from hGfap:eGFP control mice or fear-conditioned mice.
(E) Analysis of the results in (D), indicating that the amount of eGFP in astrocytes and PAPs was stable upon fear conditioning. Signals were normalized against stain-free membranes. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4 per condition); ns, not significant in an unpaired two-tailed t test.
(F) Western blot analysis of S1 (whole dorsal hippocampus extracts) and P3 (synaptogliosomes) from Aldh1l1:L10a-eGFP control mice and fear-conditioned mice.
(G) Analysis of the results in (F), indicating that the amount of eGFP-tagged ribosomes was stable in astrocytes and PAPs. The signals were normalized against stain-free membrane. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4 per condition); ns, not significant in an unpaired two-tailed t test.