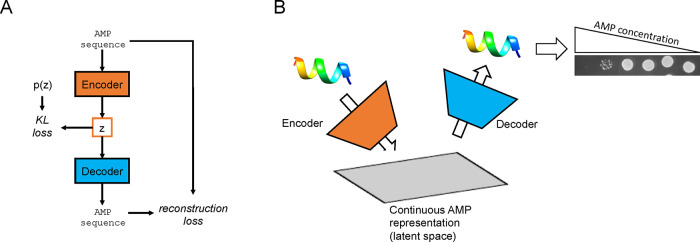
Figure 1.
Machine learning for antimicrobial design. (A) Flow diagram of VAE design. During training, both known and scrambled peptides are fed into the encoder, generating their latent codes (z). The latent codes are then decoded into the peptide sequence by the decoder. The two terms of the loss function (KL and reconstruction loss) and model are updated using stochastic gradient descent. (B) Here, we train the VAE using an AMP dataset, which allows for experimental validation of results using common microbiological assays. From starting input AMP sequences, the encoder network converts each peptide into a vector in the latent space, which can be viewed as a continuous AMP representation. Provided a point in the latent space, the decoder network will output a corresponding AMP sequence. The output sequences can then be experimentally tested for activity.