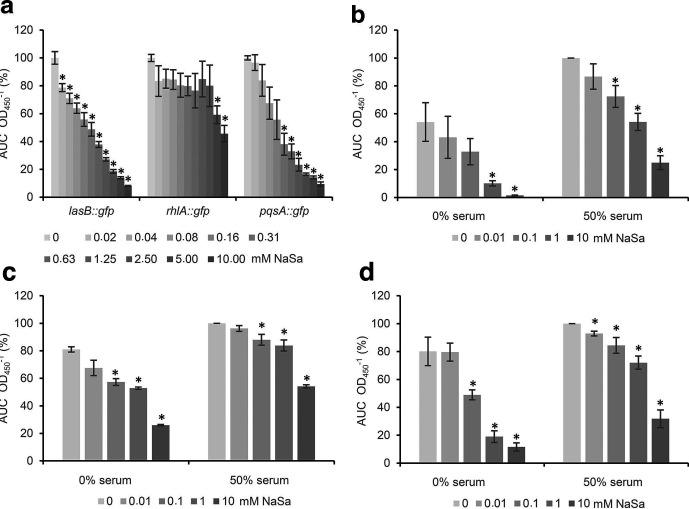
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of QS by sodium salicylate (NaSa) in P. aeruginosa . (a) Concentration-dependent effect of NaSa (0–10 mM) in AB medium on the gene expression of lasB, rhlA and pqsA evaluated with the reporter strains PAO1 lasB::gfp, rhlA::gfp and pqsA::gfp. Effect of NaSa treatment (0–10 mM) in AB media with or without 50 % serum on the expression of (b) lasB::gfp, (c) rhlA::gfp and (d) pqsA::gfp. For each group, the mean area under the curve (AUC) was calculated from each fluorescence intensity curve (baseline- and blank-adjusted) and normalized by OD from three independent experiments. Data in (a) are expressed as % of untreated control in each respective group (100 % corresponds to 4.6×107, 3.6×107 and 5.4×106 fluorescence units for lasB::gfp, rhlA::gfp and pqsA::gfp, respectively). Data in (b–d) are expressed as % of the untreated 50 % serum sample (100 % corresponds to 1.2×108, 7.0×107 and 6.8×106 fluorescence units for lasB::gfp, rhlA::gfp and pqsA::gfp, respectively). Error bars represent ±sd, N=3. * Indicates a statistically significant difference compared to untreated 0 mM NaSa group (in the 0 and 50% serum groups, respectively) with a P-value <0.05 based on one-way ANOVA Dunnett's post hoc test.