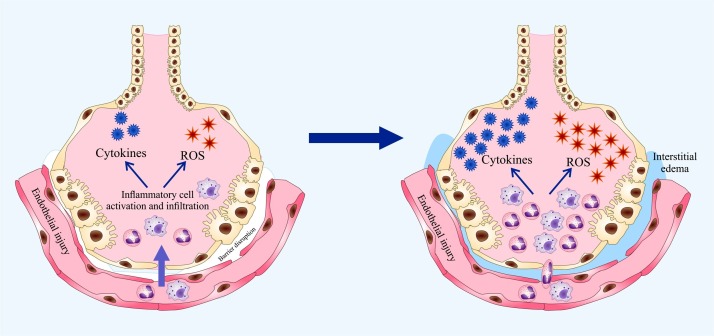
Fig. 4.
Impaired function of alveolar epithelium and microvascular endothelium in ARDS. Microvascular blood vessels allow elevated infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and macrophages into the inflamed region followed by increased release of cytotoxic factors including proinflammatory cytokines and ROS. These released mediators contribute to the endothelial and epithelial dysfunction leading to fluids leakage from the circulation into the interstitial space and alveoli. Combined, these events result in pulmonary edema and impaired gas exchange.