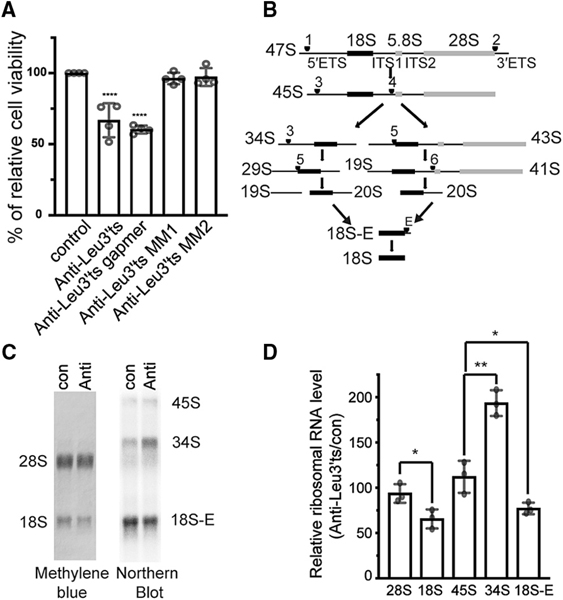
Figure 2. LeuCAG3′tsRNA Is Essential and Required for 18S rRNA Processing in Mouse Cells.
(A)Inhibition of LeuCAG3′tsRNA impairs Hepa 1–6 cell viability. Three days post-transfection, a MTS assay was performed (n = 4 independent experiments). Anti-Leu3′ts, antisense oligonucleotide to LeuCAG3′tsRNA; anti-Leu3′ts gapmer, antisense oligonucleotide that induces RNase H activity to cleave LeuCAG3′tsRNA; anti-Leu3′ts MM and MM2, two 2-nt mismatched oligonucleotides to LeuCAG3′tsRNA.
(B) Pre-rRNA processing pathways in mouse cells based on prior studies (Bowman et al., 1981; Kent et al., 2009). The 47S primary transcript is processed and categorized as 50 external transcribed spacers (5′ ETSs), 18S rRNA, internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1), 5.8S rRNA, internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2), 28S rRNA, and 3′ external transcribed spacers (3′ ETSs). There are two alternative processing pathways. Inhibition of LeuCAG3′tsRNA inhibits processing from the pre-34S to the pre-20S form depicted in pathway A. Arrowhead and number indicate cleavage sites.
(C and D) Inhibition of the LeuCAG3′tsRNA suppresses 5′ ETS processing in 18S rRNA biogenesis in Hepa 1–6 cells. Methylene blue staining (28S and 18S rRNA) and northern hybridization (45S, 34S, and 18S-E pre-rRNA) were performed with total RNA from Hepa 1–6 cells 24 h post-transfection (n = 3 in- dependent experiments). A representative image is shown in (C). Relative mature and pre-rRNA levels are shown in (D). The rRNA level from anti-Leu3′ts-transfected cells was normalized to that from con (control).
The mean is shown in (A) and (D). Error bar, SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA (A) and two-tailed t test (D). Anti, anti-LeuCAG3′tsRNA; con, control.