Figure 1:
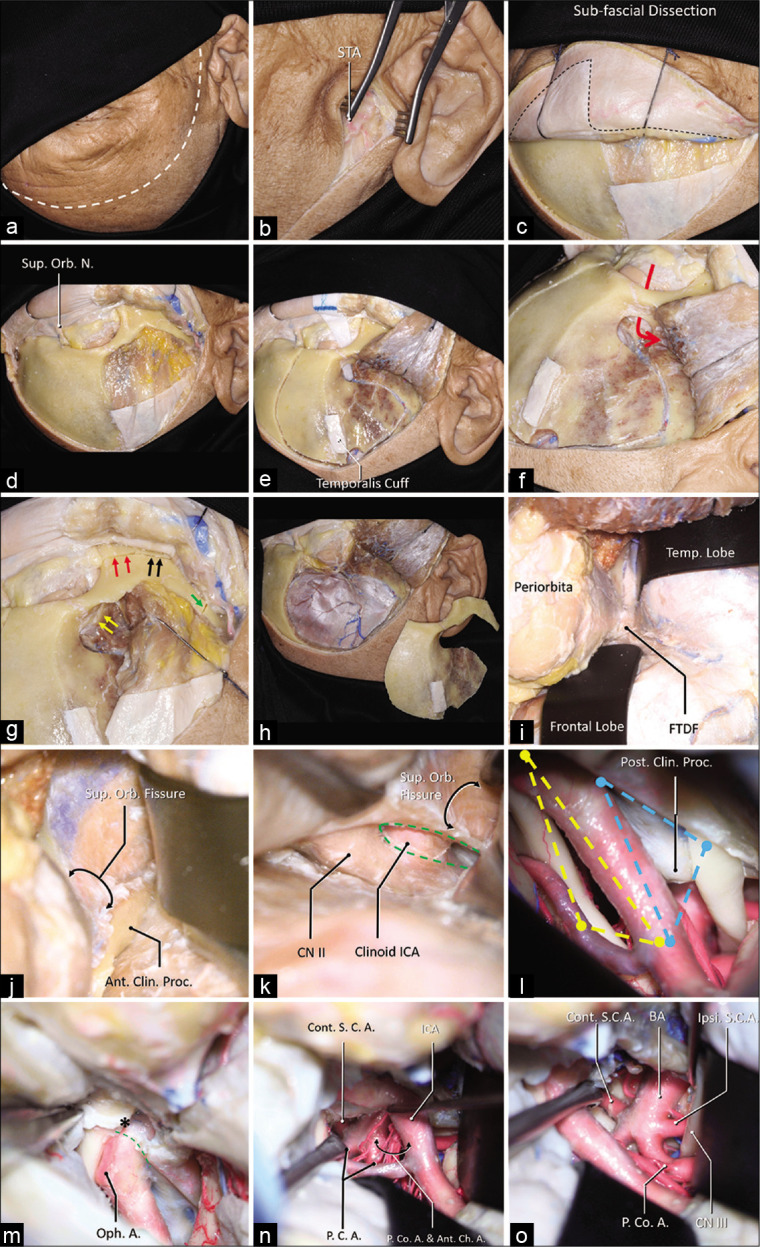
A step-by-step dissection (a) The curvilinear skin incision was demonstrated using the dashed white line, which started from 1 cm in front of the tragus and ended at the contralateral mid-pupil line. (b) The superficial temporal artery (STA) was found in the subcutaneous layer. (c) A sub-fascial dissection was performed to keep the continuation of the periosteum superior to the temporal line and the superior temporoparietal fascia inferior to the temporal line (dashed line). (d) The orbit and the zygoma were demonstrated, and the superior orbital nerve was dissected free. (e) A temporalis muscle cuff was left on the skull for reapproximation, a MacCarty keyhole at the level of the frontozygomatic suture was placed, which connects both anterior skull base and the orbit (f), the first cut was placed. (g) The MacCarty keyhole was connected to the inferior orbit fissure (yellow arrows), there were three separated cuts on the zygoma: 1, the anterior half of the zygoma was cut connecting the inferior orbital fissure (red arrows); 2, the posterior half of the zygoma was cut connecting the infratemporal fossa (black arrows); 3, the zygomatic arch was disconnected (green arrow). (h) A general view of the one-piece orbitozygomatic craniotomy. (i) After the pretemporal extradural exploration, the frontotemporal dural fold (FTDF) was demonstrated. (j) the superior orbital fissure and the nerves within were shown to be inferior to the anterior clinoid process. (k) After the anterior clinoidectomy (green dashed line), the clinoid segment of the carotid artery was demonstrated. (l) The intradural exposure showed the opitco-carotid triangle (yellow dashed line) and the carotico-oculomotor triangle (blue dashed line). (m) The distal dural ring (green dashed line) was dissected, the apex of the OCT (asterisk) was demonstrated. After the posterior clinoidectomy, the exposure to the basilar system via the OCT (n) and the COT (o) was demonstrated. Abbreviations: A., artery; Ant., anterior; Ant. Ch. A., anterior choroidal artery; BA, basilar artery; Clin., clinoid; CN, cranial nerve; Cont., contralateral; FTDF, frontotemporal dural fold; ICA, internal carotid artery; Ipsi., ipsilateral; Orb., orbital; N., nerve; Oph., ophthalmic; P.C.A., posterior cerebral artery; P. Co. A., posterior communicating artery; proc., process; S.C.A., superior cerebellar artery; STA, superficial temporal artery; Sup., superior; temp., temporal.
