Fig. 3.
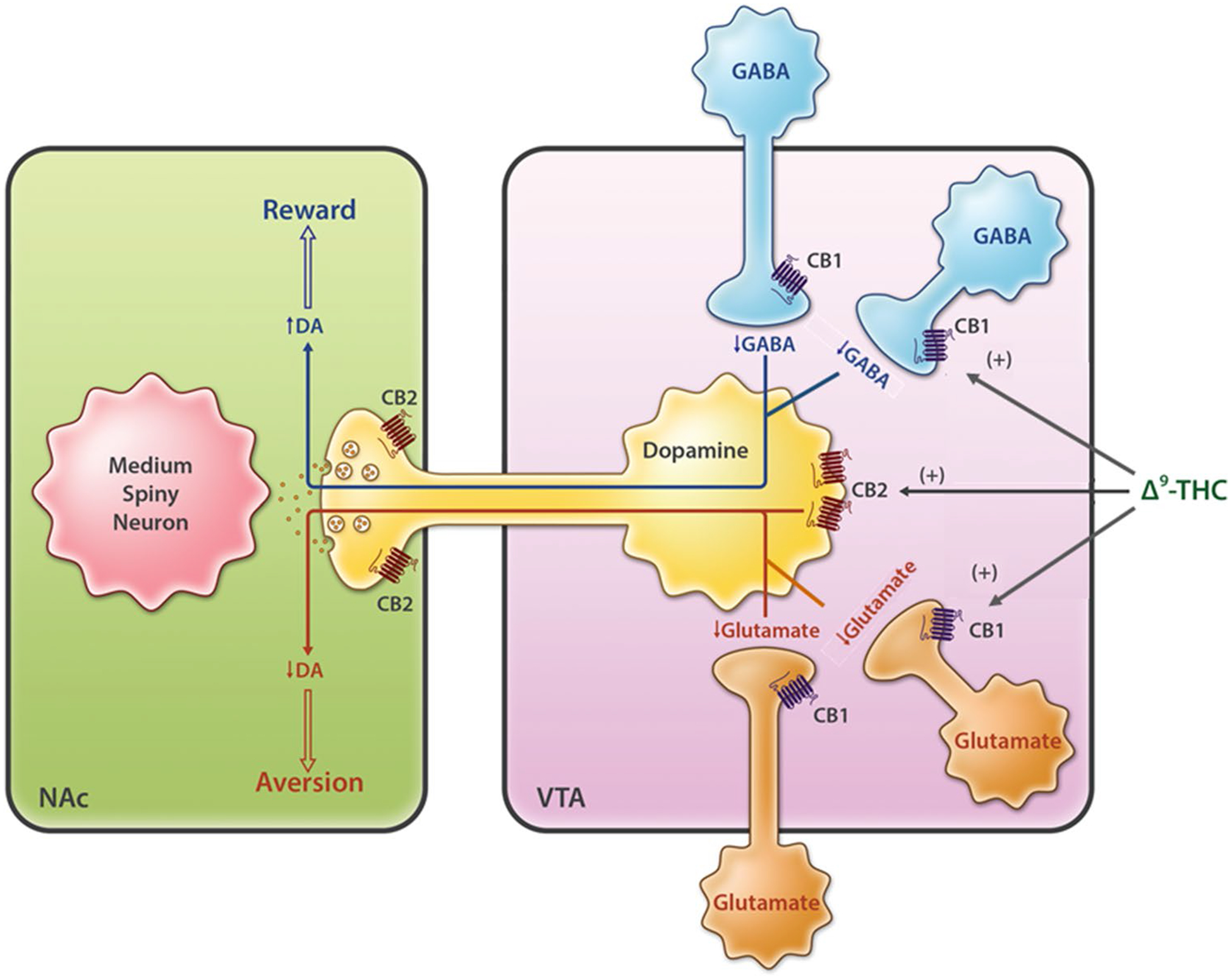
Neural mechanisms underlying cannabis reward vs. aversion. Cannabinoid CB1Rs are expressed in VTA GABAergic interneurons and glutamatergic neurons as well as their afferent projections to the VTA DA neurons, whereas CB2Rs are found in VTA DA neurons. Cannabis or cannabinoids modulate the mesolimbic DA system via activation of brain CB1Rs and CB2Rs. Cannabinoids such as Δ9-THC may produce rewarding effects by binding to CB1R on VTA GABAergic interneurons and/or their afferents, thereby reducing GABA-mediated inhibition of VTA DA neurons and increasing DA release in the NAc. Conversely, cannabinoids may produce aversive effects by activating CB1R on glutamatergic neurons in the VTA, and/or CB2Rs on DA neurons, thereby inhibiting VTA DA release to the NAc. The subjective effects of cannabinoids may thus depend on the balance of opposing CB1R and CB2R effects and individual differences in neural CB1R and CB2R expression. CB1/2R CB1/2 receptor, DA dopamine, GABA γ-aminobutyric acid, NAc nucleus accumbens, VTA ventral tegmental area, Δ9-THC Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol
