Figure 2.
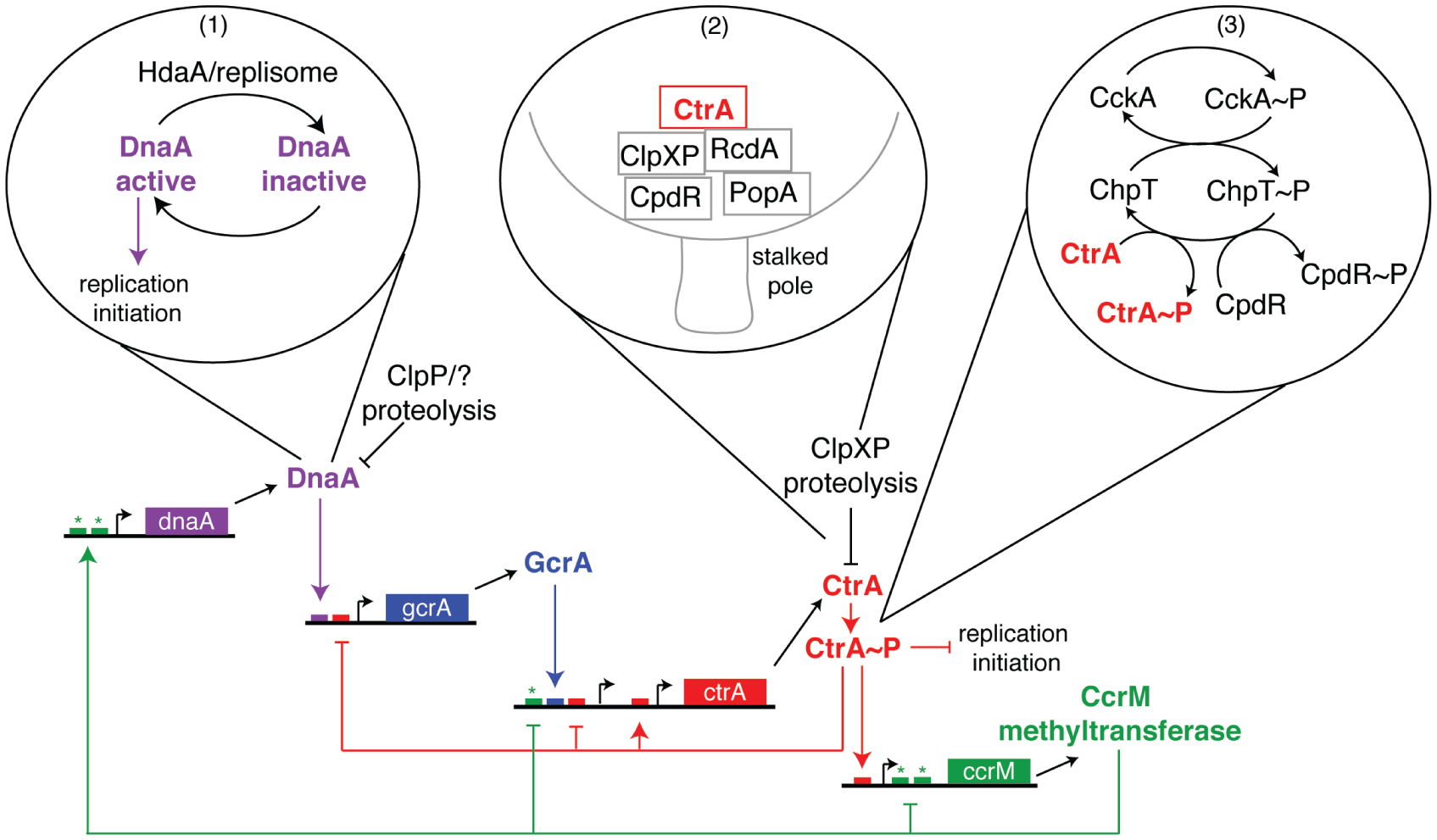
The Caulobacter core cell cycle transcriptional control circuit includes posttranslational regulation of master regulators. Each master regulator activates transcription of the next and, in the case of CtrA and CcrM, inhibits transcription of the previous master regulator in the cascade. Promoters and genes encoding the master regulators are depicted with regulatory and/or binding motifs (small boxes) indicated. The color of the regulatory motif correlates with the master regulator that governs it (i.e., small red boxes represent CtrA-binding sites, etc.). (Asterisks) CcrM methylation sites, (bubbles) posttranslational regulation of DnaA and CtrA. (1) DnaA is inactivated after HdaA joins the replisome upon initiation of replication. (2) CtrA is localized to the stalked pole, by the concerted action of RcdA, PopA, ClpXP, and CpdR, where it is subjected to ClpXP-mediated proteolysis. (3) CtrA is phosphorylated and activated by the same CckA-ChpT phosphorelay that phosphorylates and inactivates CpdR.
