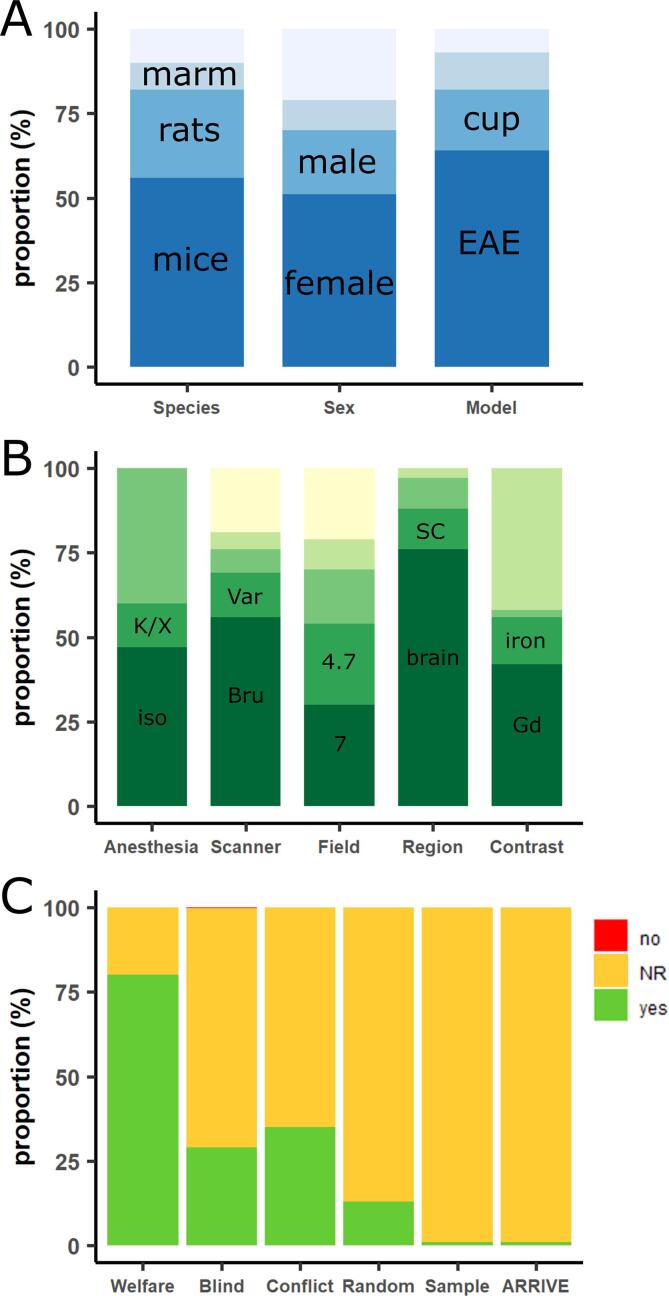
Fig. 2.
Bar plots demonstrating proportional study characteristics (A and B) and risk of bias assessment (C) of all 300 eligible studies. (A) Proportional study characteristics on species, animal sex, and multiple sclerosis animal model. (B) Proportional study characteristics on type of anesthesia for imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner supplier, field strength of MRI scanner, scanned central nervous system region(s), and use of contrast agent. The top portion of the bar always represents the remaining pooled categories per characteristic or the proportion of studies who did not report on that particular study characteristic. (C) Risk of bias assessment of eligible studies using a six-item checklist (animal welfare reporting, blinding of experiments, statement of a potential conflict of interest, randomization in experimental setup, prior sample size calculation, study in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines (Kilkenny et al., 2010, Macleod et al., 2009)). For each of these items, ‘yes’, ‘NR’ (not reported), or ‘no’ was scored. Except for the item animal welfare statement, the majority of studies have unclear risk of bias (i.e., not reported; orange bar). Abbreviations: Bru, Bruker; Cup, cuprizone; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; Gd, gadolinium; Iso, isoflurane; K/X, ketamine-xylazine; marm, marmosets; NR, not reported; Var, Varian; SC, spinal cord. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)