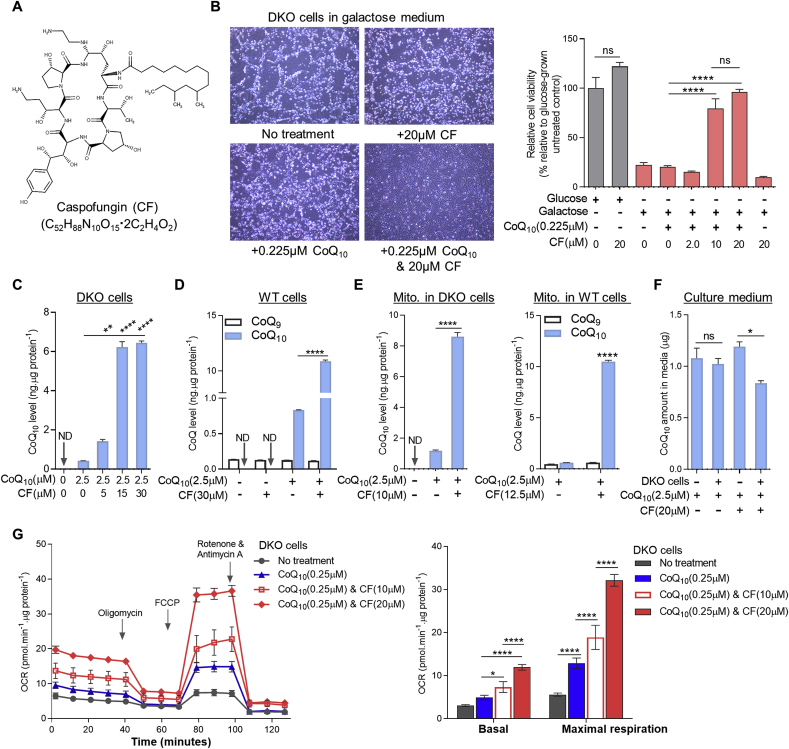
Fig. 2.
Caspofungin (CF) increases cellular uptake of exogenous CoQ. (A) Chemical structure of CF, a semi-synthetic lipopeptide composed of a cyclic hexapeptide N-linked to an acyl fatty acid side-chain. (B) Viability of DKO cells after 2 days of treatment under various conditions. Cell viability was measured by the resazurin viability assay (n = 8). See Fig. S2 for cell viability data measured by crystal violet staining. (C-D) Changes of CoQ10 levels in DKO or WT cells treated with CoQ10 and/or CF for 3 days (n = 3). (E) Mitochondrial CoQ concentrations in DKO or WT cells after 3-day treatment with either CoQ10 and/or CF (n = 3). Mito. means mitochondria. (F) Total CoQ10 amount in culture medium (10 ml per 10 cm dish) after 2 days of incubation under different conditions (n = 3). In b-f, data shown are mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test or Student's t-test was used to compare CoQ9 or CoQ10 levels between groups. (G) Comparison of the effects of CoQ10 treatment only and co-treatment of CoQ10 and CF on mitochondrial respiration of DKO cells. Representative oxygen consumption rate (OCR) traces are shown on the left. Bar graph shows summary data. Error bars represent standard deviations (SD) (n = 5). The data were subjected to two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. ND: not detectable. ns: not significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.05, and ****p < 0.0001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)