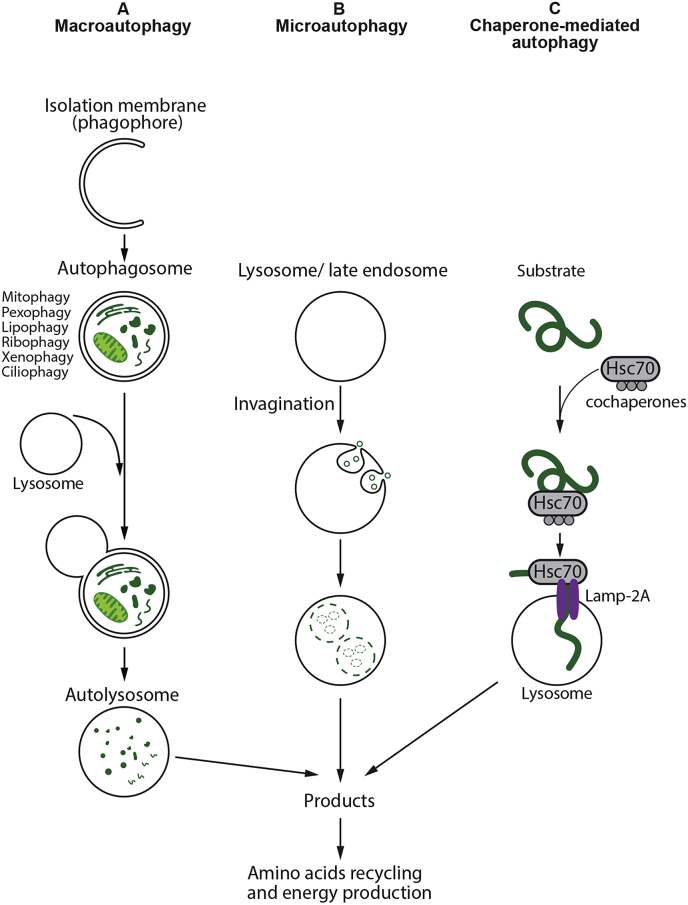
Fig. 1.
Different types of autophagy. (A) Macroautophagy: A cytosolic substrates or “cargo” is enclosed by an isolation membrane (also called phagophore) to form a double-membrane vesicles, termed autophagosomes. The outer membrane of the autophagosome fuses with the lysosome, and the internal material is degraded in the autolysosome. Macroautophagy can also target selective cargo for degradation such as organelles, proteins, microbes, and RNA. (B) Microautophagy: Small cytosolic components are directly engulfed into the lysosome or late endosomes by membrane invagination. (C) Chaperone-mediated autophagy: Substrate proteins containing a KFERQ-like motifs are recognized by chaperone Hsc70 and co-chaperones and translocated into the lysosomal lumen in a process that requires the lysosomal receptor protein LAMP-2A. After all three types of autophagy, the resultant degradation products can be used for different purposes, such as new protein synthesis or energy production.