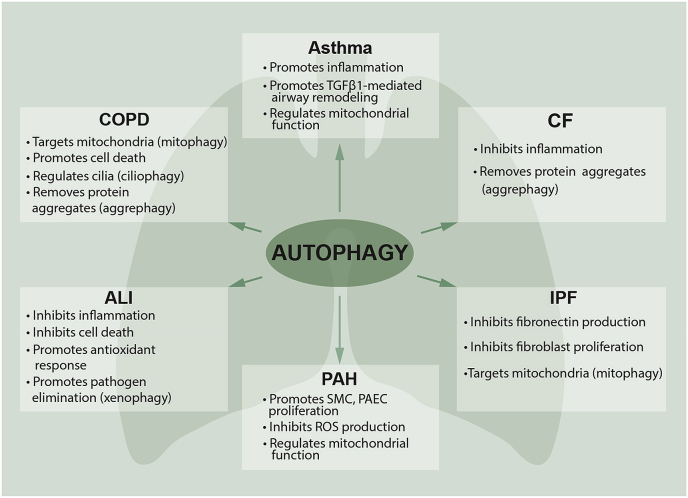
Fig. 4.
Role of autophagy in pulmonary diseases. Autophagy plays a complex role in a growing number of pulmonary diseases. Both protective and pathogenic roles for autophagy have been proposed in these diseases. Specialized functions of autophagy (selective autophagy, such as mitophagy or aggrephagy) may directly contribute to the regulation of pathogenesis in pulmonary diseases. The upregulation of autophagy may initially act as a pro-survival mechanism responsible for the clearance of damaged proteins or organelles. In the chronic lung diseases, loss of autophagy drives lung inflammation and injury, suggesting autophagy plays a protective role. However, under certain circumstances, this naturally homeostatic cellular process may become overwhelmed and ultimately become unable to deal with excessive autophagic targets leading to cell death. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ALI, acute lung injury; CF, cystic fibrosis; IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension.