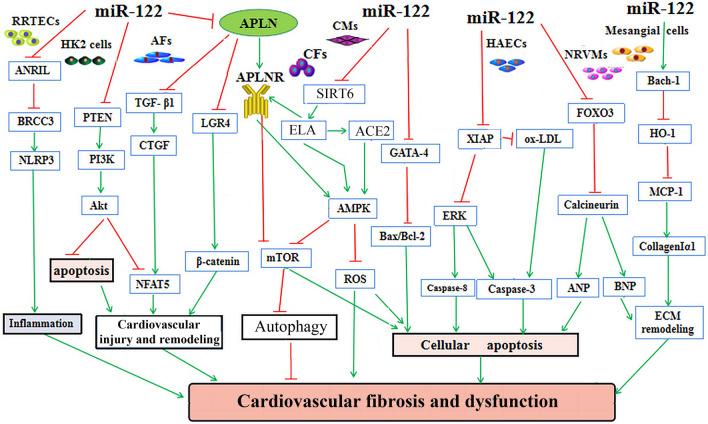
Fig. 3.
The regulatory roles and underlying mechanisms of miR-122 in cardiovascular remodeling, fibrosis and dysfunction. MiR-122 plays a role in regulating cell growth, survival, inflammation, ECM deposition, pathological remodeling, cardiovascular fibrosis and dysfunction in RRTECs, HAECs, NRVMs, CMs, AFs, CFs, and HK2 cells by modulating the ANRIL-BRCC3, FOXO3-Calcineurin, Bach-1/HO-1, TGFβ-CTGF-NFAT5 and PTEN-PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, respectively. Furthermore, the inhibition of miR-122 has been shown to modulate cardiac contractility, autophagy, apoptosis, and oxidative stress by regulating of the SIRT6-ELA-ACE2, GATA4-Bax, XIAP-ERK-Caspase, and LGR4-β-catenin signaling, respectively. ACE2 angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, AFs adventitial fibrotic cells, CFs cardiofibroblasts, CMs cardiomyocytes, HAECs, Human aortic endothelial cells, NRVMs neonatal rat cardiomyocytes, RRTECs rat renal tubular epithelial cells, HK2 cells human renal tubular epithelial cells, ANRIL antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus, BRCC3 BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex subunit 3, NLRP3nod-like receptor protein 3, PTEN gene of phosphate and tension homology deleted on chromosome ten, PI3K phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, TGF-β transforming growth factor-β, CTGF connective tissue growth factor, NFAT5 nuclear factor of activated T-cell-5, LGR4 leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 4, ROS reactive oxygen species, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, ECM extracellular matrix, AMPK adenosine 5 ‘-monophosphate-activated protein kinase, GATA4 GATA binding protein 4, SIRT6 sirtuin 6, ELA elabela, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, XIAP X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein, FOXO3 forkhead box O3, Bach-1 BTB and CNC homology 1, HO-1 heme oxygenase1, MCP-1 monocyte chemotactic protein 1