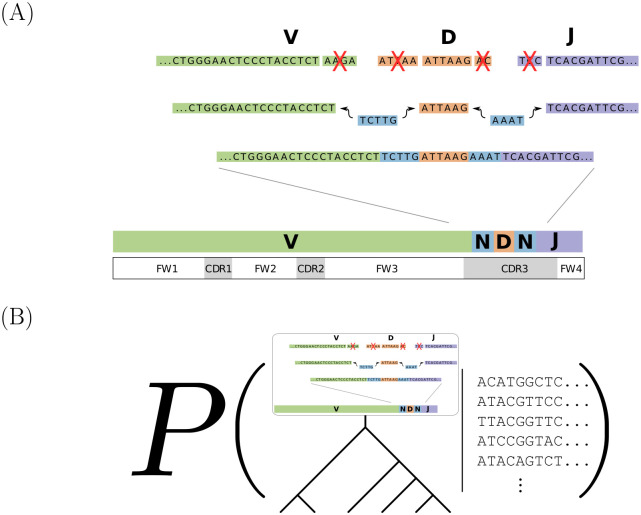
Fig 5. Model overview.
(A) A schematic representation of the naive rearrangement process from [11]. First, V (green), D (orange), and J (purple) genes are randomly selected from the respective gene pools in the body. Then, nucleotides are randomly deleted (red X’s) from both ends of the V-D and D-J junction regions and random bases (blue) are added to the same junction regions before the V, D, and J germline genes can be joined together. The BCR sequences can be partitioned into framework (FWK) and complementarity-determining (CDR) regions. (B) Our Bayesian phylo-HMM jointly models V(D)J recombination at the root of the tree (using an HMM) and then subsequent diversification (via a phylogenetic tree). We do posterior inference conditioning on the observed sequence alignment in a clonal family, but not on a fixed inferred naive sequence.