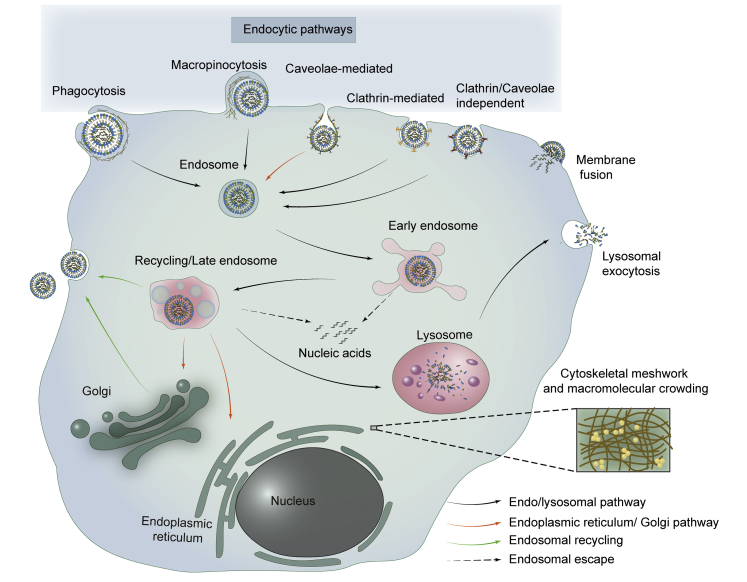
Figure 3.
Schematic Diagram of Lipoplexes Entering and Trafficking Within Cells: Entry Pathways and Intracellular Barriers
Lipoplexes enter into cells via endocytosis or membrane fusion. Endocytic pathways include clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, phagocytosis, micropinocytosis, and clathrin/caveolae-independent endocytosis. CLs must escape the endosomal entrapment before being transported to the lysosome except for membrane fusion and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Furthermore, the mesh-like cytoskeletal network and macromolecular crowding in cytoplasm impede the diffusion of lipoplexes to the nucleus.