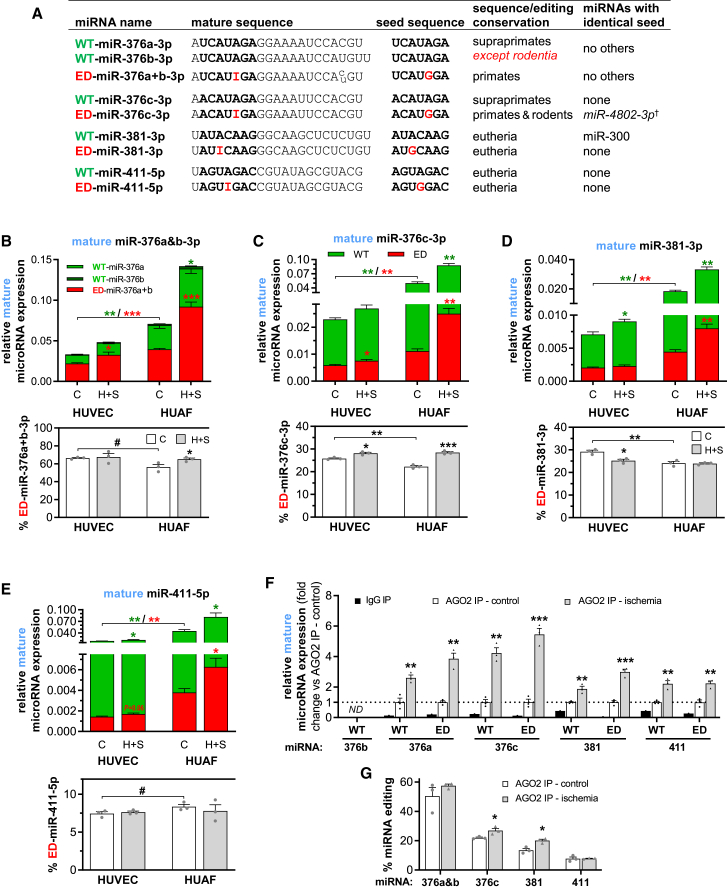
Figure 3.
Specific Quantification of Normal and Edited Mature MicroRNAs in Vascular Cells
(A) Unedited mature microRNAs (WT-microRNAs) and edited mature microRNAs (ED-microRNAs) were quantified using version-specific TaqMan qRT-PCR assays. Since inosines resulting from A-to-I editing are recognized as a G, the functional seed sequence of each microRNA is also highlighted and whether this seed is unique or shared by a different microRNA is noted. †Unvalidated microRNA according to TargetScan.16 (B–E) Relative mature WT-microRNA (green) and ED-microRNA (red) expression of (B) miR-376a&b-3p, (C) miR-376c-3p, (D) miR-381-3p, and (E) miR-411-5p in HUVECs and HUAFs cultured in control (C) conditions or hypoxia+starvation (H+S) to mimic ischemia (top panels) and the corresponding percentage of mature ED-microRNA (bottom panels). Relative microRNA expression was normalized to U6. (F) Relative expression of WT-microRNAs and ED-microRNAs in fractions after negative control IgG or AGO2 was immunoprecipitated from HUAFs cultured under control or hypoxia+starvation conditions. Data are expressed as fold change of the control AGO2 immunoprecipitation (IP). (G) Percentage editing measured in AGO2 IP fractions. All data are presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments performed with pooled cells from a total of 13 different umbilical cords. #p < 0.01, ∗∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, versus control condition unless otherwise indicated by a two-sided Student’s t test. Symbol color shows whether means of either WT or ED expression are compared.