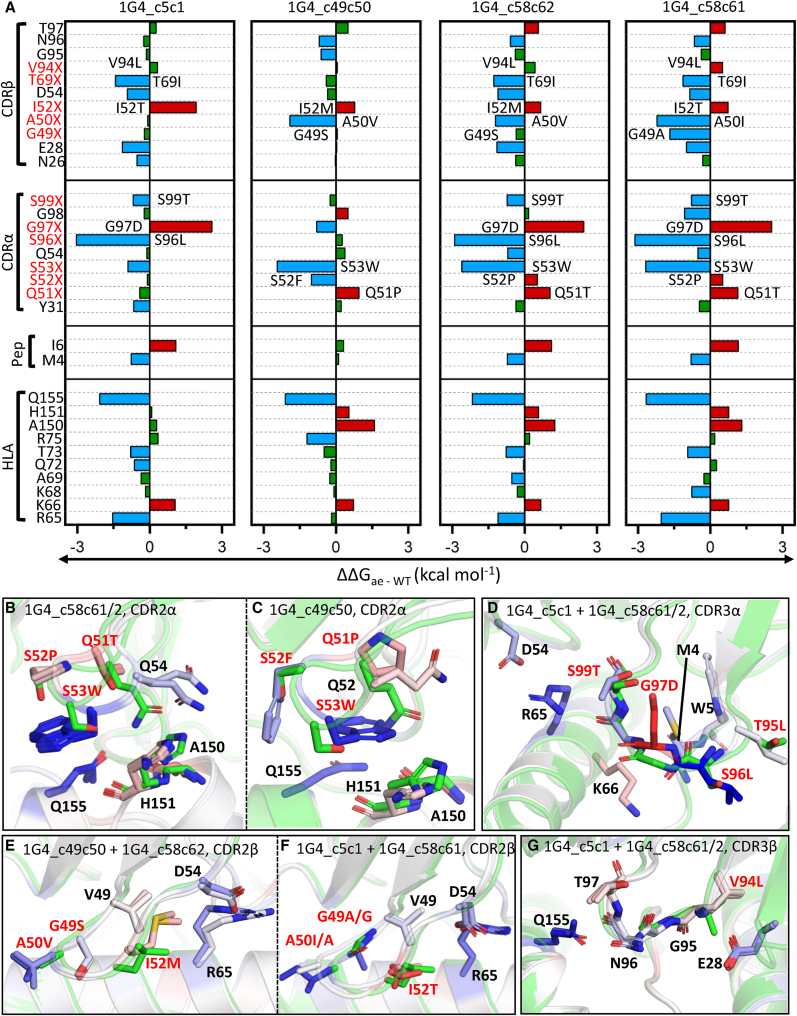
Figure 4.
The 1G4 aeTCRs Show Largely Additive Energetic Effects upon Affinity Enhancement
(A) Per-residue ΔG differences as obtained from MMGBSA analysis between the aeTCR variants and 1G4 TCRs (i.e., ΔΔG), with positions mutated indicated throughout in red. ΔΔG differences between the 1G4 TCR and aeTCRs are colored blue when ≤0.5 kcal mol–1 (favorable for binding) and red when >0.5 kcal mol–1 (unfavorable for binding), with values in between colored green. (B–G) Color mapping of the above per residue ΔΔG values onto all carbon atoms of the aeTCRs (with the 1G4 TCR structure shown in green for reference). Color mapping is performed from blue to white to red, with blue indicating a favorable change and red indicating an unfavorable change for the aeTCRs. Figures are divided to focus on the different regions of the TCR subjected to affinity maturation (CDR2α, CDR3α, CDR2β, and CDR3β), and subdivided when mutations are not consistent between aeTCRs. (B) 1G4_c58c61/2, CDR2α; (C) 1G4_c49c50, CDR2α; (D) 1G4_c5c1 + 1G4_c58c61/2, CDR3α; (E) 1G4_c49c50 + 1G4_c58c62, CDR2β; (F) 1G4_c5c1 + 1G4_c58c61, CDR2β; and (G) 1G4_c5c1 + 1G4_c58c61/2, CDR3β. (1G4_c58c61/2 means that both 1G4_c58c61 and 1G4_c58c62 TCRs are shown).