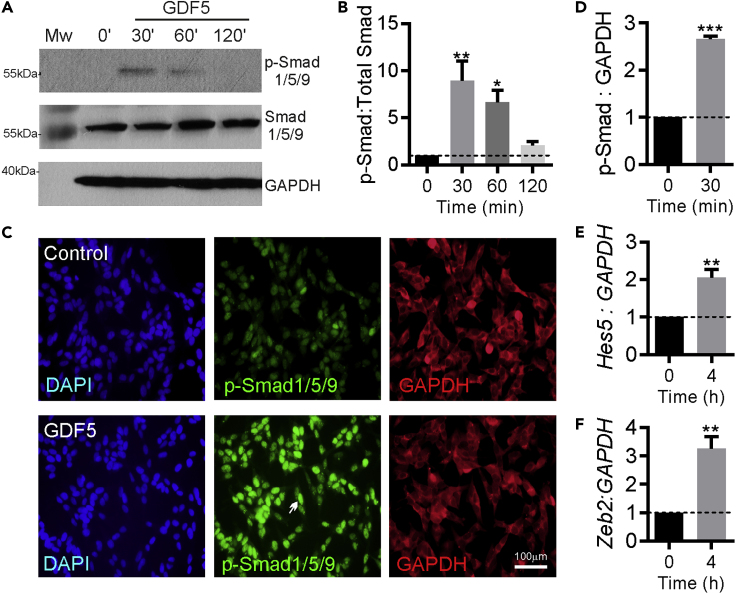
Figure 1.
GDF5 Activates Smad Signaling and Induces a Transcriptional Response in SH-SY5Y Cells
(A and B) (A) Representative western blots and (B) densitometry showing the relative level of phospho(p)-Smad1/5/9 staining, normalized to that of Smad1/5/9, in SH-SY5Y cells treated with 100 ng/mL GDF5 for 30, 60, or 120 min. Data are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 3) (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 versus control; one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test).
(C–F) (C) Representative images of p-Smad1/5/9 (green), GAPDH (red), and DAPI (blue) staining and (D) graph showing the relative level of p-Smad1/5/9 staining normalized to that of GAPDH in SH-SY5Y cells treated with 100 ng/mL GDF5 for 30 min. Real-time PCR data showing the relative expression of transcripts for (E) Hes5 and (F) Zeb2 mRNA normalized to GAPDH mRNA in SH-SY5Y cells treated with 100 ng/mL GDF5 for 4 h. Data are shown as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 3) (∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control; Student's t test).