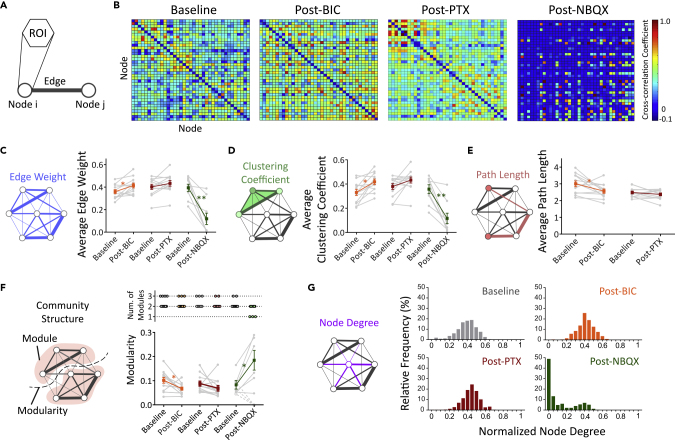
Figure 6.
Graph Theory Model-Based Characterizations of Functional Neural Networks in 3D Biomimetic Cortical Cultures
(A) The ROI was designated as a node in the graph-theory-based network analysis.
(B) Representative matrices of cross-correlation coefficients of the 3-week-old 3D cortical culture samples at baseline and post-treatment of bicuculline (BIC; 10 μM), picrotoxin (PTX; 50 μM), or NBQX (5 μM). Self-correlations were removed. The cross-correlation coefficients were then used as edge weight.
(C–F) (C) Average edge weights, (D) average clustering coefficient, (E) average path length, and (F) community structure—number of modules (top) and modularity (bottom) at baseline and post-treatments, as indicated. Post-NBQX samples that lost community structure (1 module and modularity = 0, dotted lines) were excluded from the average modularity calculation.
(G) Frequency distribution of normalized weighted node degree. For (C–F), gray data points and lines represent baseline and post-treatment measurements of individual 3D culture sample. Colored lines show mean ± SEM. (n = 9–12 samples from three to four independent experiments per group). Paired t tests were used for statistical significance comparing baseline and post-treatment of the same sample. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figures S3 and S5, and Table S1.