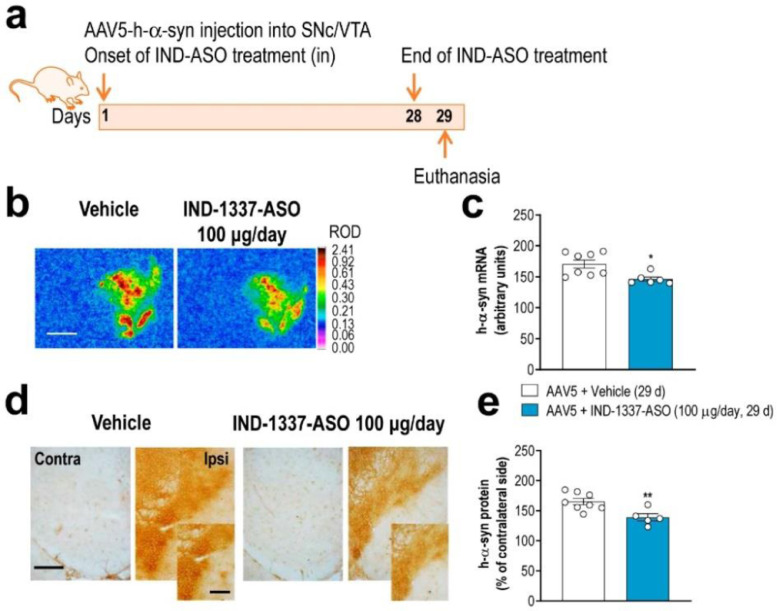
Fig. 7.
Intranasal treatment with conjugated ASO prevents AAV5-mediated h-α-syn production. (a) Treatment timeline. Mice were unilaterally injected with 1 μl AAV5 into SNc/VTA and intranasally administered with: i) vehicle or ii) IND-1337-ASO (100 μg/day) for 28 days. Mice were sacrificed 24 h later at 29 days. (b) Coronal brain sections showing h-α-syn mRNA expression in SNc/VTA of AAV5-injected mice and treated with vehicle or IND-1337-ASO assessed by in situ hybridisation procedures. Scale bar: 1 mm. Signal represents the relative optical density (ROD) of autoradiograms. (c) Decreased h-α-syn mRNA expression in AAV5-injected mice treated with IND-1337-ASO compared to control group (n = 6–8 mice/group; *P < 0.05; unpaired t-test). (d) Coronal brain sections showing h-α-syn protein levels in SNc/VTA of the same mice assessed by immunohistochemistry procedures in frozen tissue. Scale bar: low = 200 μm and high = 50 μm. (e) Reduction of h-α-syn protein level in AAV5-injected mice treated with IND-1337-ASO (n = 6–8 mice/group; **P < 0.01; unpaired t-test).