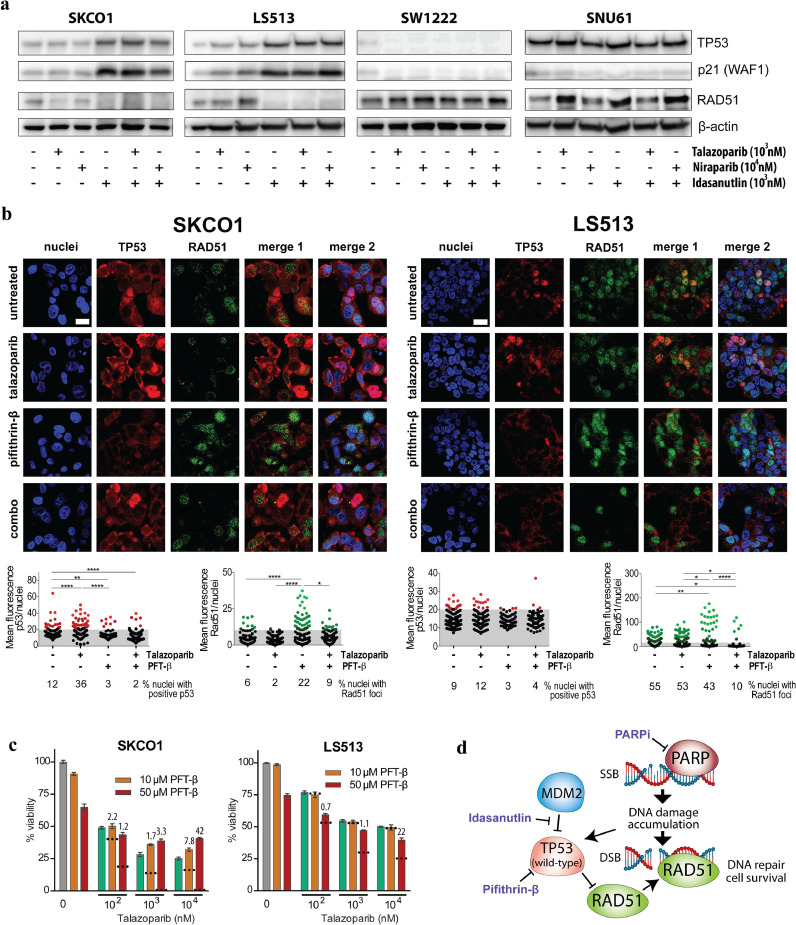
Fig. 5.
TP53 activation and regulation of RAD51 after PARP inhibition. a Western Blot analyses of TP53, p21 and RAD51 in PARP inhibitor sensitive (SKCO1 and LS513) and resistant cell lines (SW1222 and SNU61) after treatment with talazoparib, niraparib and idasanutlin for 48 h. b Representative images of TP53 expression and RAD51 foci analysed with fluorescence microscopy after 48 h treatment with 1 µM talazoparib, 50 µM pifithrin-β (PFT-β) or combination of the two. Scale bar = 20 µm. Scatter dot plots below depict analysed TP53- (red) and RAD51 (green) mean fluorescence per nuclei for the indicated treatment and cell lines, respectively. For statistical analyses, one-way ANOVA multiple comparison test with Tukey post correction was performed (****p < 0.0001, **p < 0.005, *p < 0.05). Each dot represents mean fluorescence in one nuclei and grey area indicates analysed nuclei (black) with no TP53 or RAD51 expression. c Viability of SKCO1 and LS513 cell lines after 72 h combination treatment with talazoparib and PFT-β. Values given are means ± standard error of the mean. Dotted lines indicate the predicted additive effect calculated as the sum of mean inhibitory effects from single drugs. Values above the bars for combination treatments indicate combination indexes (CI). CI < 1, CI = 1 or CI > 1 represent synergism, additive and antagonistic effects, respectively. d Schematic depiction of TP53 and RAD51 involvement after PARP inhibition in TP53 wild-type cell lines.