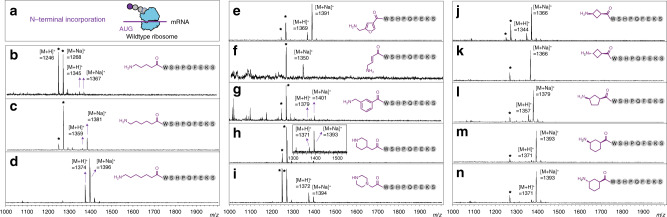
Fig. 4. Ribosomal synthesis of N-terminal functionalized peptides with backbone-extended monomers.
a All backbone-extended amino acids (3–15) charged to tRNAfMet(CAU) by Fx were incorporated into the N-terminus of a peptide by ribosome-mediated polymerization in the PURExpressTM system. The peptides were purified via the Streptavidin tag (WSHPQFEK) and characterized by MALDI mass spectrometry. The observed mass of each peptide corresponds to the theoretical mass, which is b [M + H]+ = 1345; [M + Na]+ = 1367, c [M + H]+ = 1359; [M + Na]+ = 1381, d [M + H]+ = 1373; [M + Na]+ = 1395, e [M + H]+ = 1369; [M + Na]+ = 1391, f [M + Na]+ = 1351, g [M + H]+ = 1379; [M + Na]+ = 1401, h [M + H]+ = 1371; [M + Na]+ = 1393, i [M + H]+ = 1372; [M + Na]+ = 1394, j [M + H]+ = 1343; [M + Na]+ = 1365, k [M + Na]+ = 1365, l [M + H]+ = 1357; [M + Na]+ = 1379, m [M + H]+ = 1371; [M + Na]+ = 1393, n [M + H]+ = 1371; [M + Na]+ = 1393. The peaks denoted with an asterisk are a truncated peptide not bearing the target substrate at the N-terminus ([M + H]+ = 1246; [M + Na]+ = 1268). Data are representative of three independent experiments.