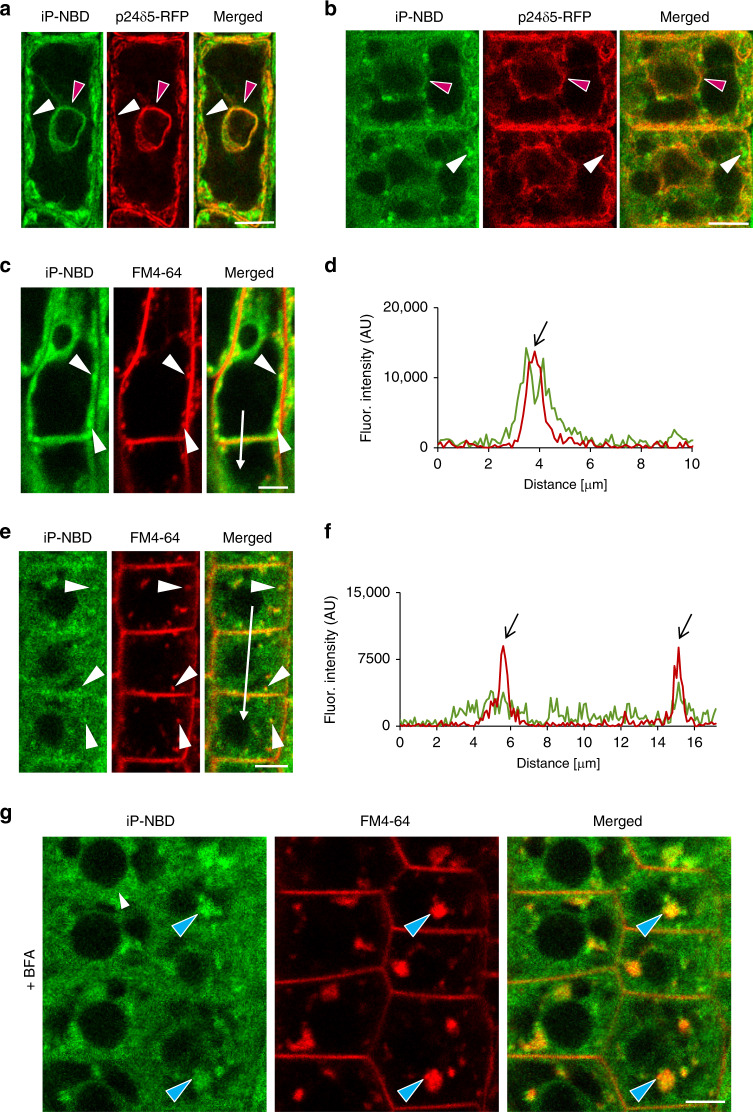
Fig. 2. Monitoring of fluorescently labelled cytokinin iP-NBD in cells of Arabidopsis root.
a, b Monitoring of fluorescently labelled cytokinin iP-NBD (green) and ER-marker p24δ5-RFP (red) in LRC cells (a) and root meristematic epidermal cells (b). iP-NBD detected partially co-localizing with p24δ5-RFP in ER (red arrowheads) and in non-ER cellular structures (white arrowheads). c–f Monitoring of iP-NBD (green) and FM4-64 (red, membrane selective dye) in LRC (c, d) and root meristematic epidermal cells (e, f). White arrowheads (c, e) indicate co-localization of iP-NBD and FM4-64 in vesicles. Profiles of fluorescence intensity distribution of both FM4-64 (red line) and iP-NBD (green line) in LRC (d) and epidermal (f) cells were measured along the white lines (c, d) starting from upper end (0 µm) towards the arrowhead. Peaks of FM4-64 fluorescence maxima (black arrows) correlate with the plasma membrane staining. iP-NBD fluorescence maximum does not overlap with FM4-64 fluorescence peak at the plasma membrane in LRC cell (d). Peaks of iP-NBD signal partially overlap with FM4-64 maxima and indicate presence of cytokinin fluoroprobe at the plasma membrane of epidermal cells (f). g Co-localization of iP-NBD and FM4-64 in endosomal compartments (blue arrowheads) formed in root meristematic epidermal cells treated with 50 µM in BFA for 1 h. Scale bars = 5 μm.