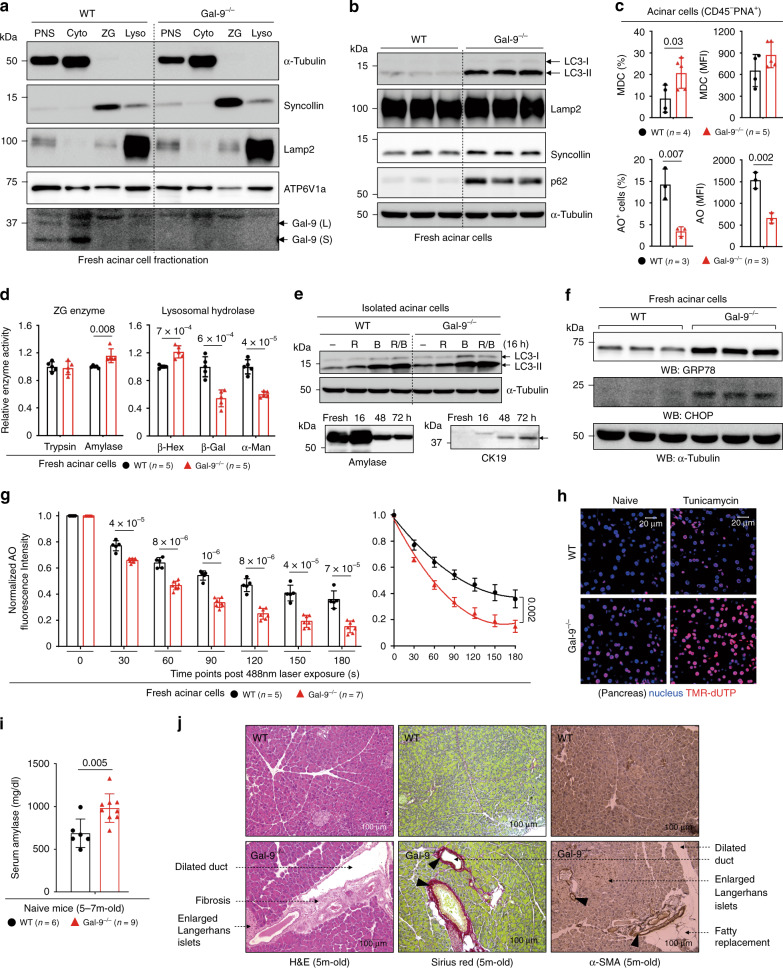
Fig. 7. Gal-9 regulates lysosomes in acinar cells to prevent pancreatic disorders.
a Western blot analysis of subcellular fractionations for localization of Gal-9 in fresh acinar cells. Cytosol marker α-tubulin, ZG marker syncollin, and lysosome marker Lamp2 are indicated. PNS: post nuclear supernatant, Cyto: cytosol fraction, Lyso: lysosome fraction. b Western blot analysis of autophagy markers in fresh acinar cells. c Flow cytometry analysis of fresh acinar cells, stained with monodansylcadaverine (MDC) to detect autophagic vacuoles or with acridine orange (AO) to detect acidic compartments. d Activity of ZG digestive enzymes or lysosomal hydrolases in fresh acinar cells was determined by specific substrates. e Western blot analysis of autophagy flux by the LC3 marker in acinar cells, treated with rapamycin (R), bafilomycin (B), or both (R/B) for 16 h. f Western blot analysis of ER stress markers in fresh acinar cells. g The indicated AO-labeled acinar cells were exposed to a 488 nm laser to induce lysosomal damage. Confocal images after laser exposure were taken at the indicated time points. Loss of lysosome stability was determined by the decrease of AO red fluorescence over time which was normalized to cells exposed at 0 s. h Immunofluorescence of pancreatic tissue sections from naïve or tunicamycin-injected mice at day-2 for TUNEL (TMR-dUTP) analysis. i Serum amylase levels were determined by Fuji Dri-Chem Clinical Chemistry Analyzer FDC 4000i.m. j Pancreatic tissues from aged mice were analyzed by H&E (left panels) for acini injury, and by Sirius red (middle panels) and α-SMA staining (right panels) for fibrosis. Data shown are representative or combined (d, i) results from two independent reproducible experiments. Statistical significance (p value) is indicated (c, d, g, i: Unpaired two-tailed t-test). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Source data are provided as a Source data file.