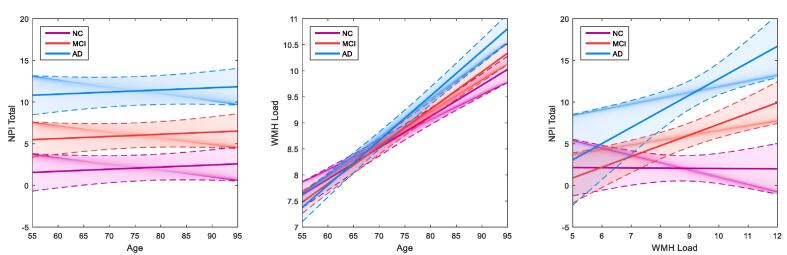
Fig. 2.
Graphs examining age, NPI total scores and WMH load in AD, MCI and normal controls. Graphs showing age not associated with NPI total scores (left), age associated with white matter hyperintensity load (centre), and the relationship between NPI total scores and WMH load (right) across AD, MCI and normal control cohorts. Age is not significantly associated with NPI total scores in any cohort (left). All groups show a positive significant association of age with higher WMH load (middle), and AD and MCI cohorts show a positive significant association between higher WMH load and greater NPI total scores (right). Solid lines indicate the estimated effect and dotted lines represent the standard error. WMH = white matter hyperintensity, NPI = neuropsychiatric inventory, AD = Alzheimer’s disease, MCI = mild cognitive impairment, NC = normal control.