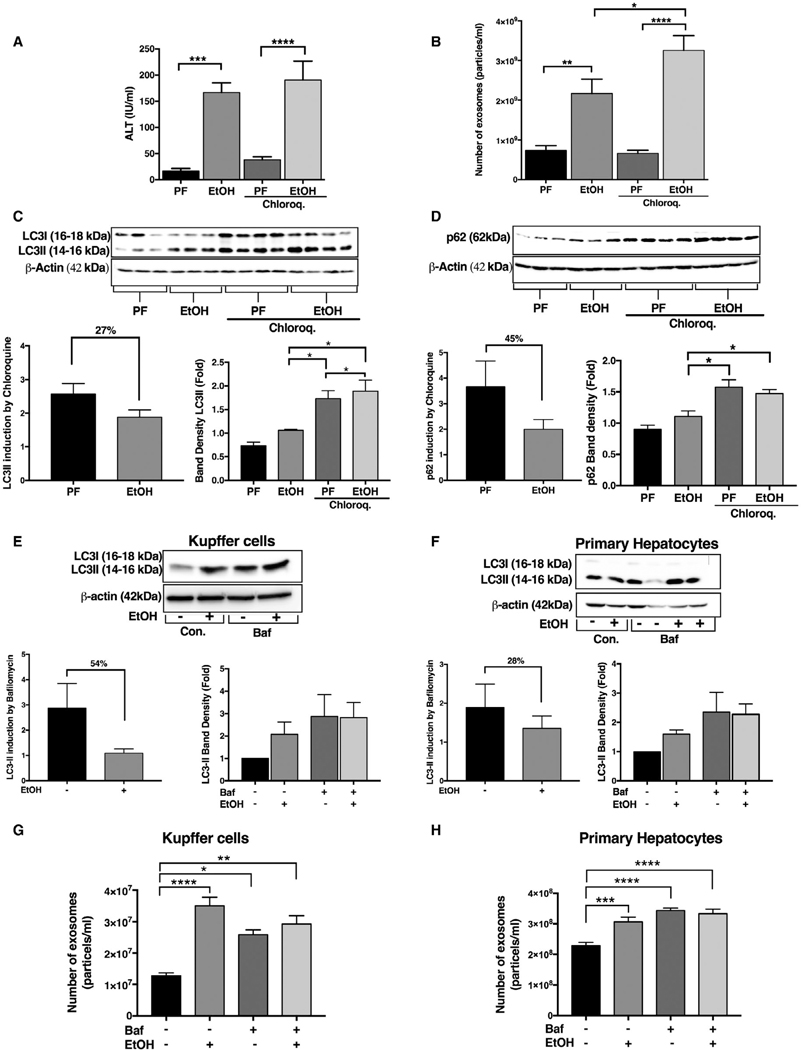
FIG. 6.
Functional block of autophagy at the autophagosome-lysosome fusion step results in increased liver injury and exosome production in acute-on-chronic alcohol feeding. Serum ALT levels were used to determine the level of liver damage in acute-on-chronic alcohol feeding (A). The number of exosomes from sera of pair-fed (PF)- and acute-on-chronic alcohol-fed (EtOH)-fed mice with or without chloroquine injection was quantified by NTA (n = 8; B). Total liver protein was extracted from PF or EtOH mice (n = 6–8) with or without 65 mg/kg of chloroquine injected intraperitonealy and analyzed by western blotting using β-actin as a loading control. Immunoblottings were probed with antibodies for LC3-I and LC3-II (C) and p62 (D). The densitometry analysis is shown as bar diagrams. The LC3-II and P62 ratio in chloroquine treated to that of untreated alcohol-fed and pair-fed animals was calculated. (C,D) KCs and primary hepatocytes were treated with and without 50 mM of alcohol for 24 hours, and bafilomycin was added (in last 12 hours) as indicated. After 24 hours, the protein levels from KCs and primary hepatocytes were analyzed by western blotting for LC3-I andLC3-II (E,F) using β-actin as a loading control. The densitometry analysis is shown as bar diagrams. The LC3-II ratio was calculated (E,F). The number of exosomes from KCs and primary hepatocytes supernatants after 24 hours was quantified by NTA (G,H). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Abbreviations: Baf, bafilomycin; Chloroq., chloroquine; Con., control.